C++ 中文周刊 第118期
公众号

RSS https://github.com/wanghenshui/cppweeklynews/releases.atom
欢迎投稿,推荐或自荐文章/软件/资源等
本周内容不多 感谢不语赞助
资讯
标准委员会动态/ide/编译器信息放在这里
编译器信息最新动态推荐关注hellogcc公众号 本周更新 2023-06-14 第206期
文章
stdexec代码中的技巧
// #include <concepts>
#include <type_traits>
// struct compile_error<What, With...>
//=====================================
struct none;
template <class What, class... With>
struct compile_error : std::false_type
{
using type = compile_error;
};
template <>
struct compile_error<none> : std::true_type
{
using type = compile_error;
};
// concept error<T>
// concept no_error<T>
//=====================================
namespace detail {
consteval compile_error<none> get_error(...);
template <class What, class... With>
consteval compile_error<What, With...> get_error(const compile_error<What, With...>*);
template <class T>
extern decltype(get_error((T*)nullptr)) error_v;
template <class T>
using error_t = decltype(error_v<T>);
template <class T>
concept error_impl = (not T{});
template <class T>
concept error = error_impl<error_t<T>>;
template <class T>
concept no_error_impl = T{};
template <class T>
concept no_error = no_error_impl<error_t<T>>;
} // namespace detail
using detail::error;
using detail::no_error;
// Usage
//=======
struct NOT_CALLABLE;
template <class T>
struct WITH_SIGNATURE;
template <class T>
struct is_function : std::conditional_t<std::is_function_v<T>,
std::true_type,
compile_error<NOT_CALLABLE, WITH_SIGNATURE<T>>>
{};
template <class T>
inline constexpr bool is_function_v = is_function<T>::value;
int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
template <class T>
#if defined(USE_COMPILE_ERROR)
requires no_error<is_function<T>>
#else
requires is_function_v<T>
#endif
void foo(T f) {
}
int main() {
foo<int(int, int)>(add);
foo(add);
}
效果
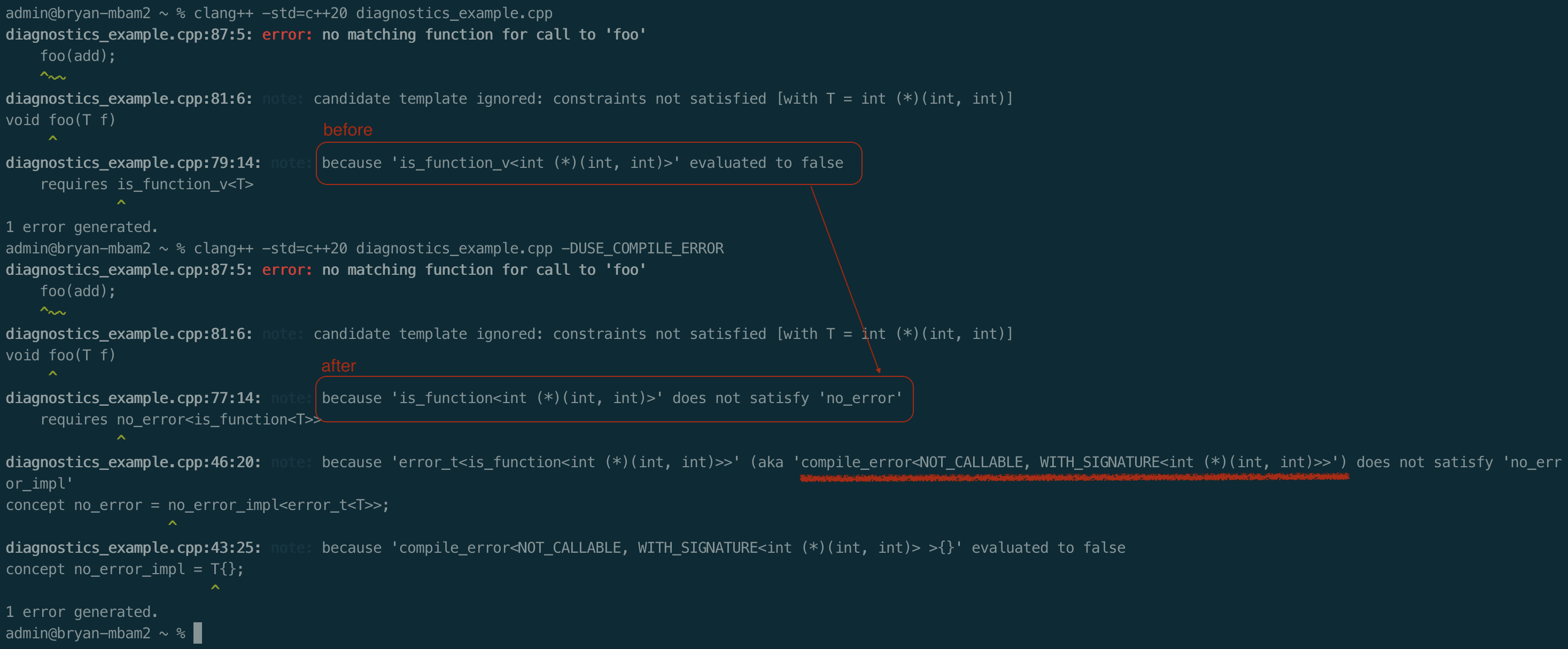
有点意思
介绍几个函数std::ranges::fold_left std::ranges::fold_left_with_iter std::ranges::fold_left_first_with_iter
贴个简单的
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
int main() {
std::vector nums {1, 2, 3, 4};
std::cout << std::ranges::fold_left(nums, 0, std::plus{});
}
/*
10
*/
#include <functional>
constexpr auto sum(auto... ts) { return (ts + ...); }
static_assert(typeid(int) == typeid(std::invoke_r<int>(&sum<short, short>, 3, 4)));
std::invoke的带返回值版本
googletest是怎么执行test的?一个全局map,把所有测试类字符串都全局注册到一个map里,其实就类似工厂函数,比如
static unique_ptr<ICompressionMethod> Create(const string& fileName) {
auto extension = GetExtension(filename);
if (extension == "zip")
return make_unique<ZipCompression>();
else if (extension = "bz")
return make_unique<BZCompression>();
return nullptr;
}
提前把zip bz注册好,这种写法肯定是不合适的,笨拙
gtest是这样的
#define GTEST_TEST_(test_case_name, test_name, parent_class, parent_id)\
class GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_case_name, test_name) \
: public parent_class { \
virtual void TestBody();\
static ::testing::TestInfo* const test_info_ GTEST_ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED_;\
};\
\
::testing::TestInfo* const GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_case_name, test_name)\
::test_info_ =\
::testing::internal::MakeAndRegisterTestInfo(\
#test_case_name, #test_name, NULL, NULL, \
new ::testing::internal::TestFactoryImpl<\
GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_case_name, test_name)>);\
void GTEST_TEST_CLASS_NAME_(test_case_name, test_name)::TestBody()
每个测试类都有个没啥用的static testinfo,用来执行注册MakeAndRegisterTestInfo
好了,来重构咱们的构造工厂
class ICompressionMethod {
public:
ICompressionMethod() = default;
virtual ~ICompressionMethod() = default;
virtual void Compress() = 0;
};
template <typename Key, typename Value, size_t Size>
struct Map {
std::array<std::pair<Key, Value>, Size> data;
size_t slot_ { 0 };
constexpr bool insert(const Key &key, const Value& val) {
if (slot_ < Size) {
data[slot_] = std::make_pair(key, val);
++slot_;
return true;
}
return false;
}
[[nodiscard]] constexpr Value at(const Key &key, const Value& none) const {
const auto itr =
std::find_if(begin(data), end(data),
[&key](const auto &v) { return v.first == key; });
if (itr != end(data)) {
return itr->second;
} else {
return none;
}
}
};
class CompressionMethodFactory {
public:
using TCreateMethod = unique_ptr<ICompressionMethod>(*)();
public:
CompressionMethodFactory() = delete;
static constexpr bool Register(string_view name,
TCreateMethod createFunc) {
if (auto val = s_methods.at(name, nullptr); val == nullptr) {
if (s_methods.insert(name, createFunc)) {
std::cout << name << " registered\n";
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
static std::unique_ptr<ICompressionMethod> Create(string_view name) {
if (auto val = s_methods.at(name, nullptr); val != nullptr) {
std::cout << "calling " << name << "\n";
return val();
}
return nullptr;
}
private:
static inline constinit Map<string_view, TCreateMethod, 4> s_methods;
};
这样,类似testinfo调用Register来注册
class ZipCompression : public ICompressionMethod {
public:
virtual void Compress() override;
static unique_ptr<ICompressionMethod> CreateMethod() {
return std::make_unique<ZipCompression>();
}
static string_view GetFactoryName() { return "ZIP"; }
private:
static inline bool s_registered =
CompressionMethodFactory::Register(ZipCompression::GetFactoryName(),
CreateMethod);
};
这个注册可能存在依赖关系,而static初始化的顺序取决于编译单元被链接后的先后顺序?constinit来保证
代码在这里 https://wandbox.org/permlink/bO5epDpOhMH8NlXQ
- The move constructor that you have to declare, even though you don’t want anyone to actually call it
class MyClass{
public:
MyClass();
// Not copyable.
MyClass(const MyClass&) = delete;
// Movable only for NRVO purposes (and RVO in C++11).
// Never implemented.
MyClass(MyClass&&);
// Not assignable.
void operator=(const MyClass&) = delete;
};
MyClass test1() {
return MyClass(); // RVO
}
MyClass test2() {
MyClass c;
return c; // NRVO
}
MyClass test3() {
MyClass c, d;
if (some_condition()) {
return c; // failed NRVO
} else {
return d; // failed NRVO
}
}
看代码,这段代码展示的是编译器尽可能的做返回值优化,但test3做不了,可能走move优化,但move只声明没实现,报错
看各位的需求了,这种场景下实现move还是值得的
视频
没啥说的。std::thread经典例子就用到这玩意了 例子在这里 https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/thread/thread/thread 不贴代码了
| 都没啥意思,也就 [Build Time Reflection with C++ in Year 2023 | Pure Virtual C++ 2023](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fXh2hVsFDso&list=PLReL099Y5nRc8Cbb_fodHFQeZ5I4N7KYo&index=16&ab_channel=MicrosoftVisualStudio) 有点意思 |
基于module的反射,之前他搞得ifc-spec 不过还没开源,倒是挺有意思
开源项目需要人手
- asteria 一个脚本语言,可嵌入,长期找人,希望胖友们帮帮忙,也可以加群753302367和作者对线
- Unilang deepin的一个通用编程语言,点子有点意思,也缺人,感兴趣的可以github讨论区或者deepin论坛看一看。这里也挂着长期推荐了
- gcc-mcf 废弃了对at&t汇编语法支持,仅支持intel汇编语法,话说at那种确实不好懂
如果有疑问评论最好在上面链接到评论区里评论,这样方便搜索,微信公众号有点封闭/知乎吞评论
