blog review 第二十九期
分片解决一切问题
eBPF: Fantastic [Network & I/O] Speeds and Where To Find Them
几个探索
XRP 注入系统内核合并系统调用 如果支持确实牛逼,相当于PGO了
BMC 网卡级别hook cache 提前响应消息。避免陷入底层
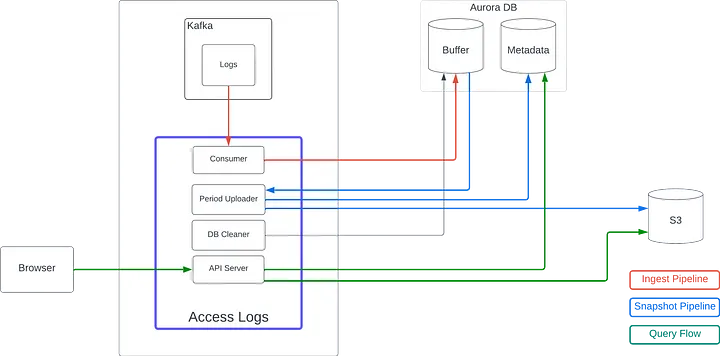
mysql + s3玩法一例
CREATE TABLE `metadata` (
`id` binary(16) NOT NULL,
`end_time_ms` bigint(20) DEFAULT NULL, # last timestamp this file contains
`file_path` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, # path of S3 file
`log_count` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, # count of the logs this S3 file contains
`last_log_id` binary(16) NOT NULL, # ULID of last log we processed
);
etcd 在超大规模数据场景下的性能优化
segregated freelist hash统计信息
分片解决所有问题
The importance of being earnestly random: Metamorphic Testing in CockroachDB
一图流
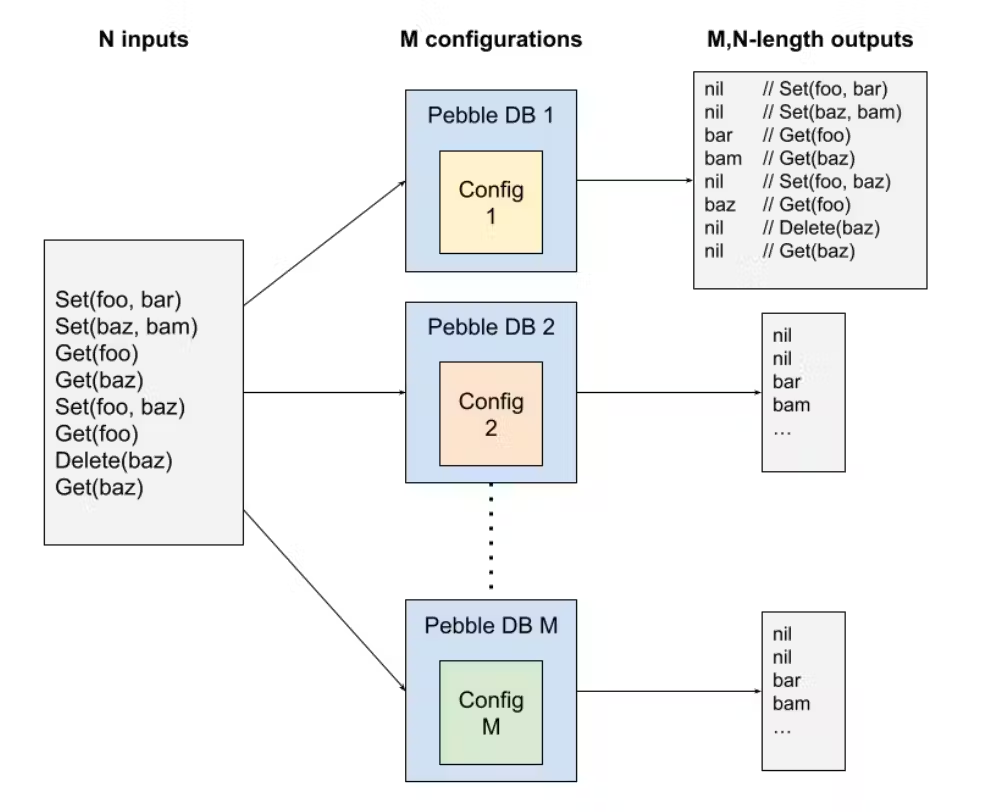
其实有一种数据库服务测试,就是双写,同时写入社区类似的服务和本地服务,对比结果。
pebble这种测试其实就是自己和自己比,对比一致性
如何基于磁盘 KV 实现 Bitmap
redis原生的思路是直接bitmap就512M
衍生的roaringbitmap的思路就是分片,不同分片使用程度不同,使用不同的编码
kvrocks的思路也是分片,毕竟是基于rocksdb的,没有采用roaring的编码思路,但是分片殊途同归吧
leetcode #2696
突然插入一道题有点生硬哈哈
class Solution {
public:
int minLength(string s) {
stack<char> stk;
for (auto i = 0; i< s.size(); i++) {
while (!stk.empty()) {
if (i >= s.size()) break;
if ((stk.top() == 'A' && s[i] == 'B') || \
(stk.top() == 'C' && s[i] == 'D') ) {
stk.pop();
cout << "pop " <<i << "\n";
i++;
} else {
break;
}
}
if (i< s.size()) {
stk.push(s[i]);
cout <<"push " <<i<<" " <<s[i] << "\n";
}
}
return stk.size();
}
};
和题解差距很大,过于局限stack,其实deque vector也是stack,更好用一些。stack这个结构不咋地
TSIDs strike the perfect balance between integers and UUIDs for most databases
https://www.foxhound.systems/blog/time-sorted-unique-identifiers/
自增bigint 优点 有序,可预测(CPU prefetch),数量大,表征时间,类似create_at,可读性好,方便看/定位 缺点,坦克问题:被摸到数据信息(简单hash混淆一下),多机时序问题(id不同)
UUID UUIDv4 8-4-4-4-12 优点 随机 自带混淆,跨系统 缺点 随机,index无法预测从而变成memory bound,体积大,浪费, 可读性差(简单hash简化一下?)
好消息,UUIDv7 https://www.ietf.org/archive/id/draft-peabody-dispatch-new-uuid-format-04.html#v7 UUID version 7 features a time-ordered value field derived from the widely implemented and well known Unix Epoch timestamp source, the number of milliseconds seconds since midnight 1 Jan 1970 UTC, leap seconds excluded. As well as improved entropy characteristics over versions 1 or 6. Implementations SHOULD utilize UUID version 7 over UUID version 1 and 6 if possible.
0 1 2 3
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| unix_ts_ms |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| unix_ts_ms | ver | rand_a |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
|var| rand_b |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
| rand_b |
+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
TSID 结合snowflake ID和ULID
ULID能排序,但不递增
Snowflake递增,但不严格排序
有着snaoflakeid一样的问题,70年
一个实现,https://github.sheincorp.cn/f4b6a3/tsid-creator
支持内置base32编码支持 https://www.crockford.com/base32.html 可读性好
横向对比
| Feature | Auto-incr. Integers | UUIDs | TSIDs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Key Type | Variable size integer | 128-bit integer | 64-bit integer |
| Uniqueness | Unique within a database | Universally unique | Unique across nodes |
| Predictability | Predictable sequence | Unpredictable | Unpredictable |
| Space Efficiency | High (small size) | Low(large size) | Moderate(larger than integers but smaller than UUIDs) |
| Data locality | High(sequential increment) | Low(random order) | High(time-sorted with random component) |
| Performance | High(efficient indexing, inserts, reads) | Poor(inefficient inserts, scattered indexes, read penalty) | High(similar to integers) |
| Readability | High(simple numbers) | Low(32 character strings) | Moderate(13 character strings) |
| Chronological Sorting | Yes, implicit(based on sequence) | No inherent order | Yes, time-sorted(based on time component) |
| Multi-node Generation | Not feasible | Easily feasible | Feasible with node IDs |
| Security (Inference Risk) | High(German Tank Problem) | Low(no inference) | Low(no inference) |
| Ease of Implementation | High(natively supported) | Moderate(varies by database) | Low(least support, requires function implementation, managing node IDs) |
| Scalability | Varies(limited by integer type) | High(no practical limit) | High(at least ~70 years, limited by timestamp size) |
| Migration Flexibility | Moderate(can change to larger integer type) | Low(hard to change key type) | High(drop-in compatible with integers) |
Leaf——美团点评分布式ID生成系统
表结构
+-------------+--------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------------+--------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
| biz_tag | varchar(128) | NO | PRI | | |
| max_id | bigint(20) | NO | | 1 | |
| step | int(11) | NO | | NULL | |
| desc | varchar(256) | YES | | NULL | |
| update_time | timestamp | NO | | CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | on update CURRENT_TIMESTAMP |
+-------------+--------------+------+-----+-------------------+-----------------------------+
biz_tag区分业务,max id + step 决定号段,不同机器攒批写入数据库
- 更新max id 获取新号段可能存在竞争
- 解决方案,提前申请 双buffer存好,监控号段消费速度
- 每个biz-tag都有消费速度监控,通常推荐segment长度设置为服务高峰期发号QPS的600倍(10分钟),这样即使DB宕机,Leaf仍能持续发号10-20分钟不受影响。
- 每次请求来临时都会判断下个号段的状态,从而更新此号段,所以偶尔的网络抖动不会影响下个号段的更新。
- 解决方案,提前申请 双buffer存好,监控号段消费速度
这个算法可能泄露订单量信息 还是得用snowflake类似方案,不过在解决时钟漂移上做了很多探索
- 依赖zk发号,发号本地存一份
- 时间检查
- 若写过,则用自身系统时间与leaf_forever/${self}节点记录时间做比较,若小于leaf_forever/${self}时间则认为机器时间发生了大步长回拨,服务启动失败并报警。
- 若未写过,证明是新服务节点,直接创建持久节点leaf_forever/${self}并写入自身系统时间,接下来综合对比其余Leaf节点的系统时间来判断自身系统时间是否准确,具体做法是取leaf_temporary下的所有临时节点(所有运行中的Leaf-snowflake节点)的服务IP:Port,然后通过RPC请求得到所有节点的系统时间,计算sum(time)/nodeSize。
- 若abs( 系统时间-sum(time)/nodeSize ) < 阈值,认为当前系统时间准确,正常启动服务,同时写临时节点leaf_temporary/${self} 维持租约。
- 否则认为本机系统时间发生大步长偏移,启动失败并报警。
- 每隔一段时间(3s)上报自身系统时间写入leaf_forever/${self}。
- 由于强依赖时钟,对时间的要求比较敏感,在机器工作时NTP同步也会造成秒级别的回退,建议可以直接关闭NTP同步。要么在时钟回拨的时候直接不提供服务直接返回ERROR_CODE,等时钟追上即可。或者做一层重试,然后上报报警系统,更或者是发现有时钟回拨之后自动摘除本身节点并报警
微信序列号生成器架构设计及演变
也是号段 + maxid模式
- 没有用mysql存,自己存文件,必然有maxid重复的问题
- 共享maxid 存储
另外就是容灾上的探索
需要仲裁者监控AllocSvr状态,以及号段接管,分配器要提供租约
- 租约失效:AllocSvr N 秒内无法从 StoreSvr 读取加载配置时,AllocSvr 停止服务
- 租约生效:AllocSvr 读取到新的加载配置后,立即卸载需要卸载的号段,需要加载的新号段等待 N 秒后提供服务
期间可能有不可服务的时间窗,业务会失败,不过会业务重试,无所谓
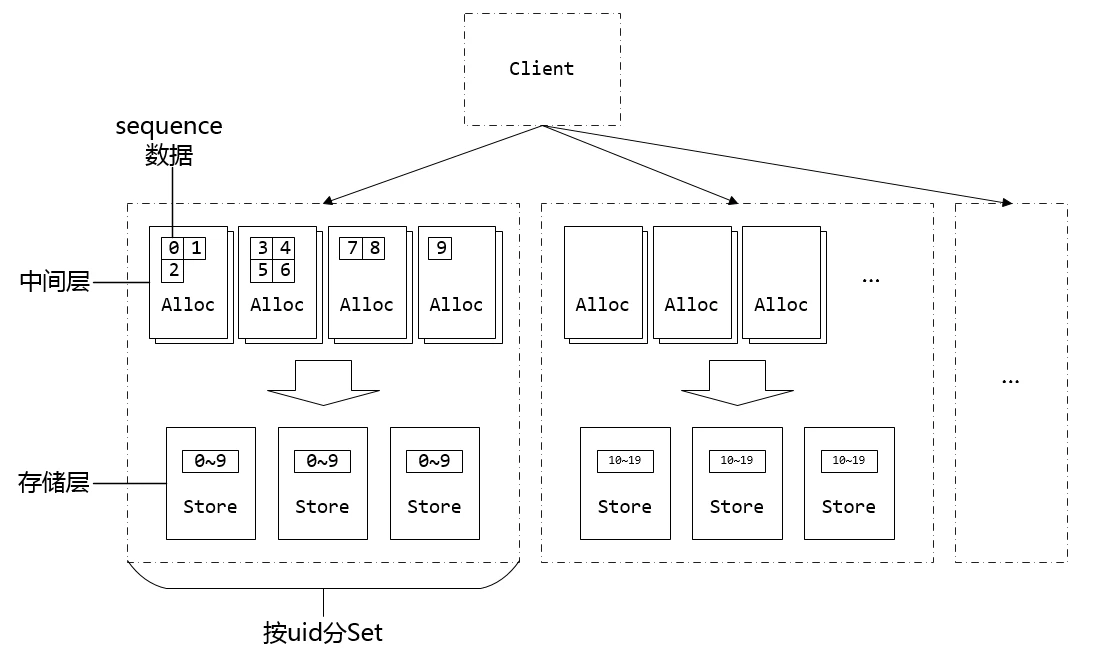
整体架构主从 + 路由表。备机主机混部,提高资源利用率
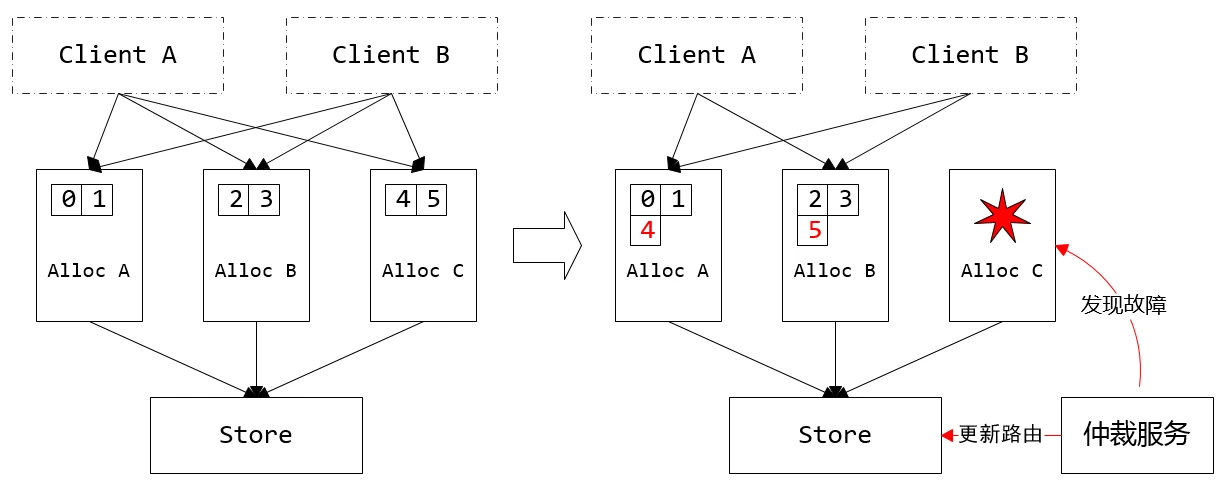
TODO
https://duanmeng.github.io/ 小伙博客不错
