fasterkv 与 fishstore
我感觉就像个bitcask加强版
而且是内存丢失版,不保证落盘的
fasterkv只是简单的kv 点读点写以及RMW
fishstore使用了faster同样的设计,为了处理json做了subset index
前面讲fasterkv,后面讲fishstore
这个记录是笔记式的,随时都可能变化
缺点
- C++代码是照着C# 代码改写的。很多系统调用都没验证错误码 io_submit错误没处理 简直离谱
- 当然使用者不验证这里的问题也是有责任的,作者需要反省自己是不是太粗心大意了
- iouring使用是最基础的用法,类似AIO,不是poll模式用法。性能根本发挥不出来
- 高级的iouring内核不经常跟进改动的话也用不上,公司的iouring支持有bug
- scan代价巨大。点读效率高,scan有bug 导致丢数据,线上出了一次问题
- rehash需要重建,基本不可接受
- 能不能优化成LF_HASH那种模式?
- compact类似scan。代价也非常巨大
- compact社区实现有bug,线上跑出了问题,也是IO报错,数据没刷下去的问题
- hash index内存占用太大,对于离线写在线读的场景,直接读index文件,靠pagecache抗
- 开链,一部分数据在LOG文件上,读取IO带来的开销很大,如果是静态表,应该把hash链全放在内存中或者集中在一个文件中
- 其实可以离线构建的时候遍历一遍,生成链表hint文件
- 如果当成静态表使用,为啥不用完美hash构建?完美hash有内存缺陷无法构建?
- 开链,一部分数据在LOG文件上,读取IO带来的开销很大,如果是静态表,应该把hash链全放在内存中或者集中在一个文件中
线上使用的是离线写在线读的模式,有增量场景,这种用法其实和完美hash构造差不多。唯一区别,能捡个现成的用
- 如果是全量,对比完美hash构建表,写入能快多少?
- 特别是大量数据,完美hash针对大量数据,可能需要把key都加载到内存吧,这种也不太可接受
[toc]
基本概念
一个hashtable构成的hybird log hashtable 以cache line对齐避免false sharing
hybird log相当于一个内部维护的页子系统,负责映射地址以及罗盘内存
可以理解成一个大号的hashtable,但是还支持部分落盘,且无锁,速度快
对比redis,显然能支持更多的数据,redis只能支持内存大小的数据,多了没地儿放
对比memcache也是同样的问题,memcache是个大号的LRU。并且也是不支持scale的,多线程工作也快不了哪里去
对比rocksdb,点读性能不行,但是牺牲了范围查
对比bitcask,更快。bitcask更倾向于只读不改的文件存储,且bitcask没有快照等复杂的功能,就是个存储
对于一个db的分析
- 架构
- 基本CURD功能路径
- 文件相关 备份恢复等等
- 数据评估:内存消耗等等
架构
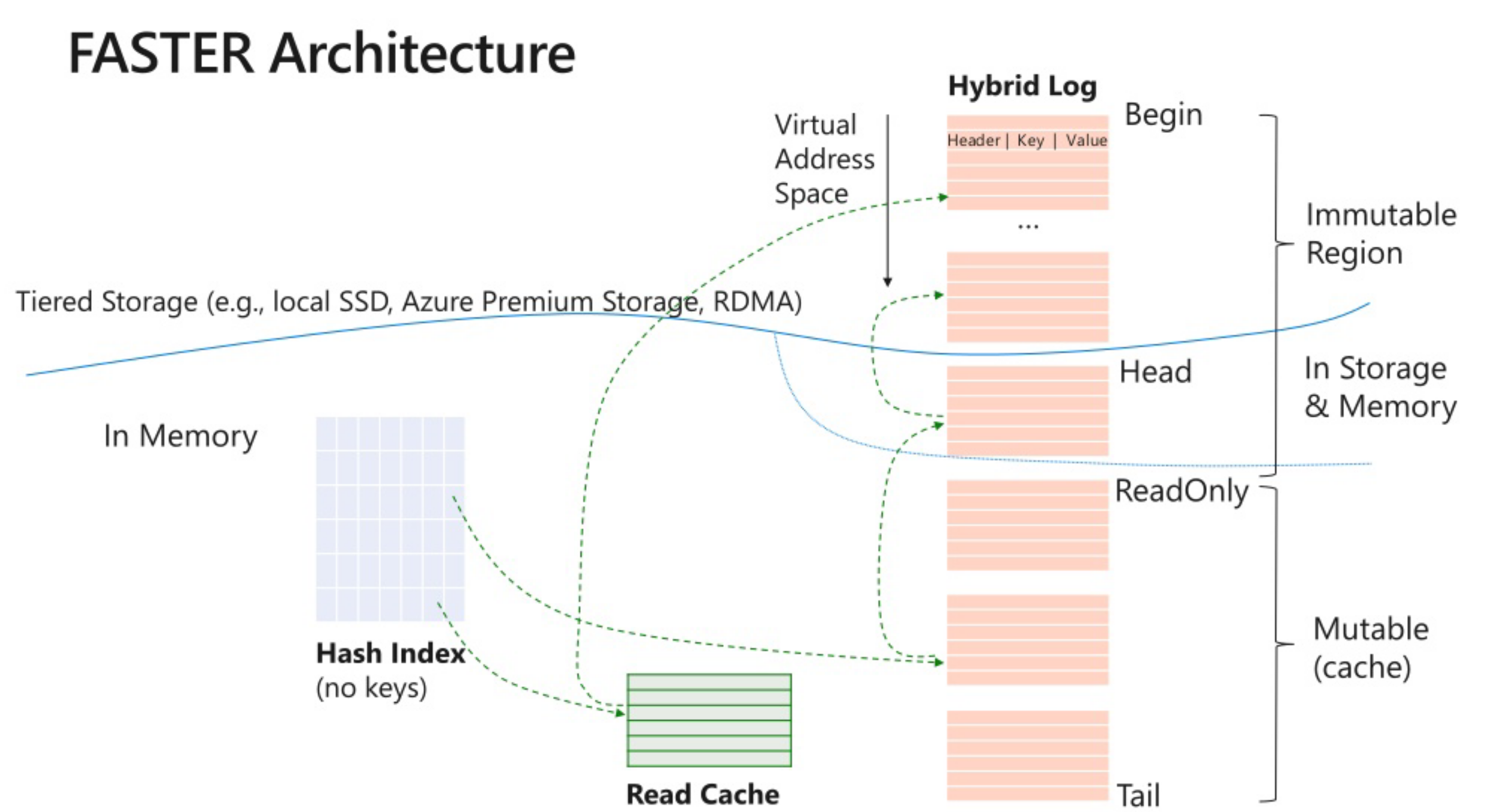
主要逻辑论文这个图描述就足够了
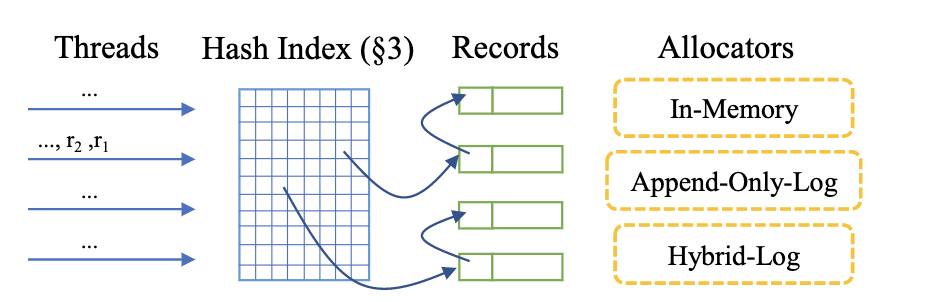
Hybrid log是一段内存,可以当成circular buffer,通过page状态来刷新推进
fastkv store设计
private:
// 推进版本号
LightEpoch epoch_;
public:
disk_t disk;
hlog_t hlog;
private:
static constexpr bool kCopyReadsToTail = false;
static constexpr uint64_t kGcHashTableChunkSize = 16384;
static constexpr uint64_t kGrowHashTableChunkSize = 16384;
bool fold_over_snapshot = true;
/// Initial size of the table
uint64_t min_table_size_;
// Allocator for the hash buckets that don't fit in the hash table.
// hash撞了的key放这里 后缀ofb
MallocFixedPageSize<HashBucket, disk_t> overflow_buckets_allocator_[2];
// An array of size two, that contains the old and new versions of the hash-table
InternalHashTable<disk_t> state_[2];
CheckpointLocks checkpoint_locks_;
ResizeInfo resize_info_;
AtomicSystemState system_state_;
/// Checkpoint/recovery state.
CheckpointState<file_t> checkpoint_;
/// Garbage collection state.
GcState gc_;
/// Grow (hash table) state.
GrowState grow_;
/// Global count of pending I/Os, used for throttling.
std::atomic<uint64_t> num_pending_ios;
/// Space for two contexts per thread, stored inline.
ThreadContext thread_contexts_[Thread::kMaxNumThreads];
InternalHAshtable 两份,经典double buffer,方便版本新旧更新
比如这种https://github.com/apache/incubator-brpc/blob/master/src/butil/containers/doubly_buffered_data.h
address设计
class Address {
///
/// An invalid address, used when you need to initialize an address but you don't have a valid
/// value for it yet. NOTE: set to 1, not 0, to distinguish an invalid hash bucket entry
/// (initialized to all zeros) from a valid hash bucket entry that points to an invalid address.
static constexpr uint64_t kInvalidAddress = 1;
/// A logical address is 8 bytes.
/// --of which 48 bits are used for the address. (The remaining 16 bits are used by the hash
/// table, for control bits and the tag.)
// 64位 48位用来做地址,16预留给hashtable
// 地址组成 page + page offset,通过page index定位page
static constexpr uint64_t kAddressBits = 48;
static constexpr uint64_t kMaxAddress = ((uint64_t)1 << kAddressBits) - 1;
/// --of which 25 bits are used for offsets into a page, of size 2^25 = 32 MB.
// page offset预留位
static constexpr uint64_t kOffsetBits = 25;
static constexpr uint32_t kMaxOffset = ((uint32_t)1 << kOffsetBits) - 1;
/// --and the remaining 23 bits are used for the page index, allowing for approximately 8 million
/// pages.
// page index预留位
static constexpr uint64_t kPageBits = kAddressBits - kOffsetBits;
static constexpr uint32_t kMaxPage = ((uint32_t)1 << kPageBits) - 1;
////
union {
struct {
uint64_t offset_ : kOffsetBits; // 25 bits
uint64_t page_ : kPageBits; // 23 bits
uint64_t reserved_ : 64 - kAddressBits; // 16 bits
};
uint64_t control_;
};
};
利用了位域来省空间, 做到cacheline对齐,避免 false sharing
AtomicAddress是Address的原子封装
FixedPageAddress
类似Address,给MallocFixedPageSize用的
/// A fixed-page address is 8 bytes.
/// --of which 48 bits are used for the address. (The remaining 16 bits are used by the hash
/// table, for control bits and the tag.)
static constexpr uint64_t kAddressBits = 48;
static constexpr uint64_t kMaxAddress = ((uint64_t)1 << kAddressBits) - 1;
/// --of which 20 bits are used for offsets into a page, of size 2^20 = 1 million items.
static constexpr uint64_t kOffsetBits = 20;
static constexpr uint64_t kMaxOffset = ((uint64_t)1 << kOffsetBits) - 1;
/// --and the remaining 28 bits are used for the page index, allowing for approximately 256
/// million pages.
static constexpr uint64_t kPageBits = kAddressBits - kOffsetBits;
static constexpr uint64_t kMaxPage = ((uint64_t)1 << kPageBits) - 1;
union {
struct {
uint64_t offset_ : kOffsetBits; // 20 bits
uint64_t page_ : kPageBits; // 28 bits
uint64_t reserved : 64 - kAddressBits; // 16 bits
};
uint64_t control_;
};
keyhash
/// Hash of a key is 8 bytes, compatible with hash bucket entry.
struct KeyHash {
KeyHash()
: control_{ 0 } {
}
explicit KeyHash(uint64_t code)
: control_{ code } {
}
KeyHash(const KeyHash& other)
: control_{ other.control_ } {
}
KeyHash& operator=(const KeyHash& other) {
control_ = other.control_;
return *this;
}
/// Truncate the key hash's address to get the page_index into a hash table of specified size.
//快速算size的余数,当且仅当size是2的幂才有效
inline uint64_t idx(uint64_t size) const {
assert(Utility::IsPowerOfTwo(size));
return address_ & (size - 1);
}
/// The tag (14 bits) serves as a discriminator inside a hash bucket. (Hash buckets use 2 bits
/// for control and 48 bits for log-structured store offset; the remaining 14 bits discriminate
/// between different key hashes stored in the same bucket.)
inline uint16_t tag() const {
return static_cast<uint16_t>(tag_);
}
private:
union {
struct {
uint64_t address_ : 48;
uint64_t tag_ : 14;
uint64_t not_used_ : 2;
};
uint64_t control_;
};
};
这里 address tag都是key 的hash的一段
idx表示用key的大小来做分段,能分的
hash表如何决定具体的entry?
inline HashBucket& bucket(KeyHash hash) {
return buckets_[hash.idx(size_)];
}
idx根据一段hash算出这段hash的特征值,也就是size的余数到bucket的某个槽,然后tag也是hash的一段,这两个来保证不冲突
Epoch
epoch基本概念
全局epoch current_epoch E
线程entry自己的epoch local_current_epoch ET
safe epoch,所有的epoch都大于的epoch
safe_to_reclaim_epoch Es 表示最大的那个safe epoch,也就是所有epoch中最小的那个 -1
EpochAction
Acquire 申请Entry 初始化ET为E
Refresh 更新ET ES 触发ready action
BumpEpoch 推进E 注册新的action
Release 移除Entry
Q:kMaxNumThreads = 96写死的,这个和什么有关系?
entry是cacheline对齐的
epoch初始化
void Initialize(uint32_t size) {
num_entries_ = size;
// do cache-line alignment
table_ = reinterpret_cast<Entry*>(aligned_alloc(Constants::kCacheLineBytes,
(size + 2) * sizeof(Entry)));
new(table_) Entry[size + 2];
current_epoch = 1;
safe_to_reclaim_epoch = 0;
for(uint32_t idx = 0; idx < kDrainListSize; ++idx) {
drain_list_[idx].Initialize();
}
drain_count_ = 0;
}
/// List of action, epoch pairs containing actions to performed when an epoch becomes
/// safe to reclaim.
EpochAction drain_list_[kDrainListSize];
/// Count of drain actions
std::atomic<uint32_t> drain_count_;
Q: 为什么多分配两个?
访问/刷新,通过protect
/// Enter the thread into the protected code region
/// Process entries in drain list if possible
inline uint64_t ProtectAndDrain() {
uint32_t entry = Thread::id();
table_[entry].local_current_epoch = current_epoch.load();
if(drain_count_.load() > 0) {
Drain(table_[entry].local_current_epoch);
}
return table_[entry].local_current_epoch;
}
这里的threadid,通过preserveEntry初始化
inline static uint32_t ReserveEntry() {
#ifdef COUNT_ACTIVE_THREADS
int32_t result = ++current_num_threads_;
assert(result < kMaxNumThreads);
#endif
uint32_t start = next_index_++;
uint32_t end = start + 2 * kMaxNumThreads;
for(uint32_t id = start; id < end; ++id) {
bool expected = false;
if(id_used_[id % kMaxNumThreads].compare_exchange_strong(expected, true)) {
return id % kMaxNumThreads;
}
}
// Already have 64 active threads.
throw std::runtime_error{ "Too many threads!" };
}
/// The current thread's page_index.
static thread_local ThreadId id_;
/// Next thread index to consider.
static std::atomic<uint32_t> next_index_;
/// Which thread IDs have already been taken.
static std::atomic<bool> id_used_[kMaxNumThreads];
注意这里id_used只有kMaxNumThreads大小,没用上预留的2,
注意id_used_的遍历方式,,这个endkMaxNumThreads*2,是一个经典的ring-buffer的循环遍历,比如从最后开始遍历,通过这个end和mod能遍历回来
回到Drain
这里通过ComputeNewSafeToReclaimEpoch来更新epoch
CPR concurrent prefix recovery
这里在一个记录中保存两个数据版本,一个stable和一个live。另外有一个整数来保存当前的版本。一个稳定的状态下面,数据处于一个版本 v。一个CPR commit操作会将这个版本v变为v+1。算法分为几个步骤执行:prepare, in-progress and wait-flush。为了支持算法的运行,这里维护两个全局的变量 Global.phase和Global.version,分别表示数据库当前的状态和版本。每个线程会拷贝这些信息一个线程局部的版本,只会在epoch synchronization更新线程局部的信息,减少同步的开销
四个状态
REST Commit在数据处于rest phase状态的时候被请求。设这个时候数据的版本为v。这个阶段由Commit函数触发。这个函数中更新数据库的状态为prepare,并添加一个PrepareToInProg。这个tigger会在所有的线程进入prepare状态后触发。每个线程也会更新本地的保存的信息。之后进入prepare阶段
PREPARE 准备版本推进 这里如果遇到了大于目前版本V的数据版本,这个事务的执行abort。这个线程会更新线程本地的信息
IN-PROGRESS 执行版本推进 PrepareToInProg函数会在所有的线程进入prepare状态之后被触发。它会更新系统的状态为in-progress,然后添加另外的一个trigger,刷新本地的信息。一个In-Progress状态的线程在数据版本为v+1的状态下面执行事务。这个操作的时候,如果一个线程遇到去读写记录集合内,且版本小于v+1的,它会将这些记录的版本信息修改为v+1。这么处理的原因是为了其它线程防止读取到这些还没有提交的数据。为了相互操作的不Blocking。这里会将记录live的数据拷贝到stable部分中。
WAIT-FLUSH 等待版本下盘 InProgToWaitFlush操作。这个操作会首先设置全局状态信息为wait-flush。如果对于版本信息为v+1的记录,收集起stable版本,否则收集live版本。这个时候进来的事务会按照在in-progress阶段中处理的方式一样处理,所有的记录被收集且持久化之后,更新状态为rest,并更新全局的版本信息为v+1
流程图
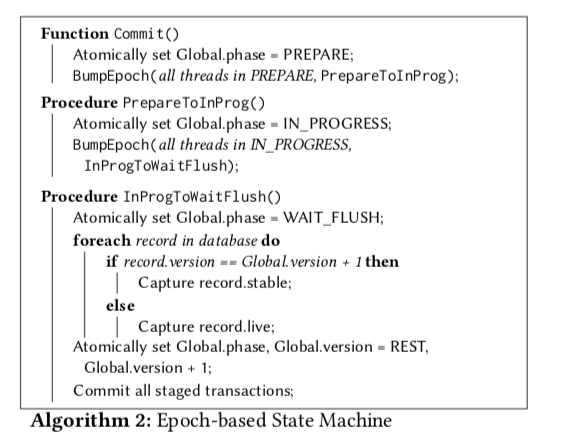
这是论文描述的状态,实际上的状态已经复杂成这样了, 新的状态流转后面再整理
/// Phases, used internally by FASTER to keep track of how far along FASTER has gotten during
/// checkpoint, gc, and grow actions.
enum class Phase : uint8_t {
/// Checkpoint phases.
PREP_INDEX_CHKPT,
INDEX_CHKPT,
PREPARE,
IN_PROGRESS,
WAIT_PENDING,
WAIT_FLUSH,
REST,
PERSISTENCE_CALLBACK,
/// Garbage-collection phases.
/// - The log's begin-address has been shifted; finish all outstanding I/Os before trying to
/// truncate the log.
GC_IO_PENDING,
/// - The log has been truncated, but threads are still cleaning the hash table.
GC_IN_PROGRESS,
/// Grow-index phases.
/// - Each thread waits for all other threads to complete outstanding (synchronous) operations
/// against the hash table.
GROW_PREPARE,
/// - Each thread copies a chunk of the old hash table into the new hash table.
GROW_IN_PROGRESS,
INVALID
};
Checkpoint
一个checkpoint的文件结构
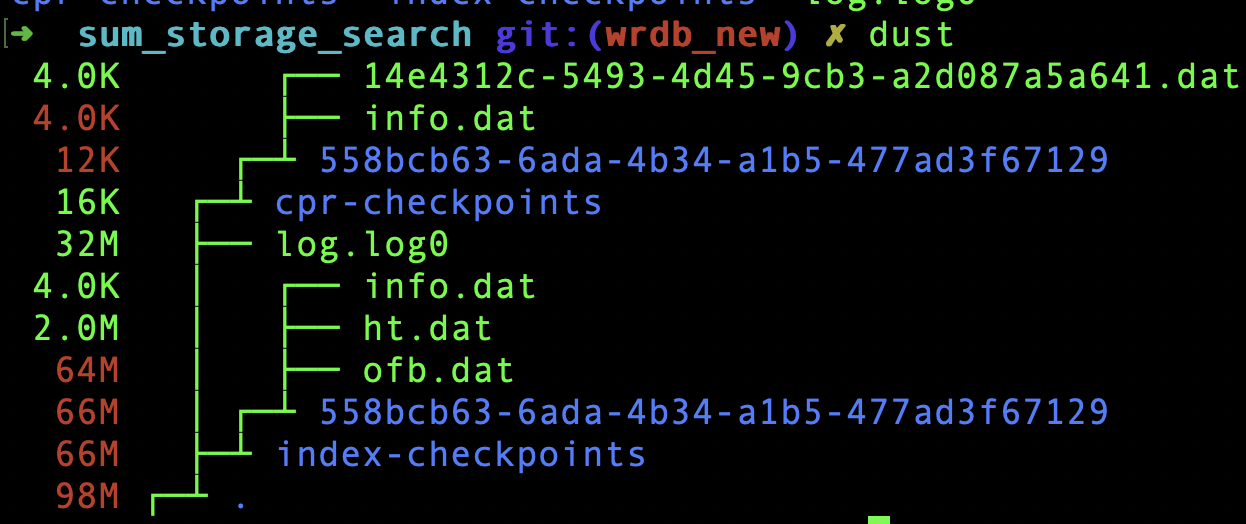
简单数学
假定1亿条数据,每条数据256字节(k+v) 数据大小大概24G
总共的数据条数如何计算?
checkpoint_.index_metadata.ofb_count
对应的meta数据这里贴出来
这也就解释了这些文件的来源
通过 ReadIndexMetadata/ReadCprContexts/ReadCprMetadata来做个打印
log_meta:use_snapshot_file: 0
version: 1
num_threads: 1
flushed_address: 140734493459720
final_address: 140734493459728
PersistentExecContext:
serial_num 1048575 version: 1 guid: 14e4312c-5493-4d45-9cb3-a2d087a5a641
index_meta:
version: 1
table_size: 32768
num_ht_bytes: 2097152
num_ofb_bytes: 8757056
ofb_count: 136829
log_begin_address: 140734493459736
checkpoint_start_address: 140734493459744
其中info.dat 对应的是log meta和index meta
ht.dat对应的hashtable的持久化
ofb.dat对应的 overflowbucket的持久化
checkpoint lock
进入checkpoint状态会加锁
CheckpointLocks是一个AtomicCheckpointLock数组,初始化根据多少个hash创建多少个锁
AtomicCheckpointLock就是封装CheckpointLock,CheckpointLock比较常规
union {
struct {
uint32_t old_lock_count_;
uint32_t new_lock_count_;
};
uint64_t control_;
};
一个是旧的版本锁,一个是新的版本锁
同时只能锁一个,对应count++,解锁对应count–,当且仅当另一个锁没有上锁的时候才能有动作
/// Try to lock the old version of a record.
inline bool try_lock_old() {
CheckpointLock expected{ control_.load() };
while(expected.new_lock_count_ == 0) {
CheckpointLock desired{ expected.old_lock_count_ + 1, 0 };
if(control_.compare_exchange_strong(expected.control_, desired.control_)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
inline void unlock_old() {
control_ -= CheckpointLock{ 1, 0 } .control_;
}
CheckpointLocks看看初始化和get就可以了
void Initialize(uint64_t size) {
assert(size < INT32_MAX);
assert(Utility::IsPowerOfTwo(size));
if(locks_) {
aligned_free(locks_);
}
size_ = size;
locks_ = reinterpret_cast<AtomicCheckpointLock*>(aligned_alloc(Constants::kCacheLineBytes,
size_ * sizeof(AtomicCheckpointLock)));
std::memset(locks_, 0, size_ * sizeof(AtomicCheckpointLock));
}
inline AtomicCheckpointLock& get_lock(KeyHash hash) {
return locks_[hash.idx(size_)];
}
checkpoint_status,以及主体流程
faster内部持有checkpoint_status维护状态,且这个类提供创建接口
主要流程
- Checkpoint
- 判定SystemState是否满足条件
epoch_.ResetPhaseFinished();- uuid生成,目录生成(两个,一个index一个实际数据)
checkpoint_.InitializeCheckpoint- 判定fold_over_snapshot,如果是,重置flush_pending
index_metadata.Initialize标记hybrid_log_persistence_callbacklog_metadata.Initialize标记index_persistence_callback
InitializeCheckpointLockscheckpoint_locks_.Initialize
- 更改SystemState 结束
-
CheckpointHybridLog- 判定SystemState是否满足条件
epoch_.ResetPhaseFinished();- uuid生成,目录生成
checkpoint_.InitializeHybridLogCheckpoint- 判定fold_over_snapshot,如果是,重置flush_pending
- 标记hybrid_log_persistence_callback , index_persistence_callback置空
InitializeCheckpointLocks- 更改SystemState 结束
-
CheckpointIndex- 判定SystemState是否满足条件
epoch_.ResetPhaseFinished();checkpoint_.InitializeIndexCheckpoint- 标记index_persistence_callback, hybrid_log_persistence_callback 置空
- 更改SystemState 结束
-
Recover
-
判定SystemState是否满足条件
-
checkpoint_.InitializeRecoverindex和hyperlog的token -
ReadIndexMetadata- 直接复制给
checkpoint_.index_metadata
- 直接复制给
-
ReadCprMetadata -
直接赋值给
checkpoint_.log_metadata -
校验
checkpoint_.log_metadata.version == checkpoint_.index_metadata.version -
ReadCprContextsPersistentExecContext,就三个字段,guid,serial_num, version,拿到serial_num记录下当前块auto result = checkpoint_.continue_tokens.insert({context.guid, context.serial_num});
-
RecoverFuzzyIndex()这里用到了index_metadata记录的各种size - 重建hastable
file_t ht_file = disk.NewFile(disk.relative_index_checkpoint_path(checkpoint_.index_token) + "ht.dat")state_[hash_table_version].RecoverInternalHashTable<D>::Recover
- 重建overflow 桶file_t
ofb_file =disk.NewFile(disk.relative_index_checkpoint_path(checkpoint_.index_token) + "ofb.dat");overflow_buckets_allocator_.RecoverMallocFixedPageSize<T, F>::Recover
-
RecoverFuzzyIndexComplete- state_ ,
InternalHashTable<D>::RecoverCompletedisk_->TryComplete();ioHandler.TryComplete()->QueueIoHandler::TryComplete()
- overflow_buckets_allocator_
MallocFixedPageSize<T, F>::RecoverCompletedisk_->TryComplete();ioHandler.TryComplete()->QueueIoHandler::TryComplete()
- Clear all tentative entries.
// Clear all tentative entries. for(uint64_t bucket_idx = 0; bucket_idx < state_[hash_table_version].size(); ++bucket_idx) { HashBucket* bucket = &state_[hash_table_version].bucket(bucket_idx); while(true) { for(uint32_t entry_idx = 0; entry_idx < HashBucket::kNumEntries; ++entry_idx) { if(bucket->entries[entry_idx].load().tentative()) { bucket->entries[entry_idx].store(HashBucketEntry::kInvalidEntry); } } // Go to next bucket in the chain HashBucketOverflowEntry entry = bucket->overflow_entry.load(); if(entry.unused()) { // No more buckets in the chain. break; } bucket = &overflow_buckets_allocator_[hash_table_version].Get(entry.address()); assert(reinterpret_cast<size_t>(bucket) % Constants::kCacheLineBytes == 0); } } - state_ ,
-
根据fold_over_snapshot来调用RecoverHybridLog/RecoverHybridLogFromSnapshotFile, 默认fold_over_snapshot=true
-
读这个区域
Address to_address = checkpoint_.log_metadata.final_address; Address from_address = checkpoint_.index_metadata.checkpoint_start_address; uint32_t start_page = from_address.page(); uint32_t end_page = to_address.offset() > 0 ? to_address.page() + 1 : to_address.page(); uint32_t capacity = hlog.buffer_size(); -
hlog.AsyncReadPagesFromLog (PersistentMemoryMalloc) 从file中读page,读num个
- AsyncReadPages
- 判定读读page的指针是否合法
Page(start_page),不合法分配一个pageAllocatePage(start_page)合法就填零 - 标记当前page的状态为发起读
recovery_status.page_status(read_page).store(PageRecoveryStatus::IssuedRead) - 更新一下pagestatus的访问状态
PageStatus(read_page).LastFlushedUntilAddress.store(Address{read_page + 1, 0}); - read_file.ReadAsync 开始读,填到对应的page内存上,这个file是外部初始化好的disk透出来的log_file_t
- FileSystemSegmentedFile::ReadAsync
- 根据source确定segment,如果本地指针是空,或者不包含这个segment,就主动OpenSegment(segment)
- 如果指针不是空且不包含这个segment,直接创建segment,FileSystemSegmentBundle
- handler_t::async_file_t.Open(handler),直接打开文件
- QueueFile::Open
- File::Open
- QueueFile::Open
- handler_t::async_file_t.Open(handler),直接打开文件
- 如果指针不是空且不包含这个segment,直接创建segment,FileSystemSegmentBundle
- 根据source确定segment,如果本地指针是空,或者不包含这个segment,就主动OpenSegment(segment)
- FileSystemSegmentedFile::ReadAsync
- 判定读读page的指针是否合法
- AsyncReadPages
-
循环RecoverFromPage
-
循环AsyncFlushPage
-
循环查page状态FlushDone
-
-
RestoreHybridLog
- 又读一遍,范围
Address tail_address = checkpoint_.log_metadata.final_address; uint32_t end_page = tail_address.offset() > 0 ? tail_address.page() + 1 : tail_address.page(); uint32_t capacity = hlog.buffer_size(); // Restore as much of the log as will fit in memory. uint32_t start_page; if(end_page < capacity - hlog.kNumHeadPages) { start_page = 0; } else { start_page = end_page - (capacity - hlog.kNumHeadPages); } RecoveryStatus recovery_status{ start_page, end_page }; -
checkpoint_.RecoverDone();
- index_metadata.Reset(); log_metadata.Reset(); snapshot_file.Close();
- system_state_.store(SystemState{Action::None, Phase::REST, checkpoint_.log_metadata.version + 1});
-
- RecoverFromPage 这个比较暴力,指定地址就行了,这个是在Recover内部调用的
hybrid_log_persistence_callback何时调用
case Phase::PERSISTENCE_CALLBACK:
assert(current_state.action != Action::CheckpointIndex);
// Handle WAIT_FLUSH -> PERSISTENCE_CALLBACK and PERSISTENCE_CALLBACK ->
// PERSISTENCE_CALLBACK
if (previous_state.phase == Phase::WAIT_FLUSH) {
// Persistence callback
if (checkpoint_.hybrid_log_persistence_callback) {
checkpoint_.hybrid_log_persistence_callback(Status::Ok,
prev_thread_ctx().serial_num);
}
// Thread has finished checkpointing.
thread_ctx().phase = Phase::REST;
// Thread ack that it has finished checkpointing.
if (epoch_.FinishThreadPhase(Phase::PERSISTENCE_CALLBACK)) {
GlobalMoveToNextState(current_state);
}
}
break;
index_persistence_callback何时调用
switch (next_state.action) {
case Action::CheckpointFull:
case Action::CheckpointIndex:
case Action::CheckpointHybridLog:
switch (next_state.phase) {
case Phase::PREPARE:
// Index checkpoint will never reach this state; and CheckpointHybridLog() will handle
// this case directly.
assert(next_state.action == Action::CheckpointFull);
// INDEX_CHKPT -> PREPARE
// Get an overestimate for the ofb's tail, after we've finished fuzzy-checkpointing the
// ofb. (Ensures that recovery won't accidentally reallocate from the ofb.)
checkpoint_.index_metadata.ofb_count =
overflow_buckets_allocator_[resize_info_.version].count();
// Write index meta data on disk
if (WriteIndexMetadata() != Status::Ok) {
checkpoint_.failed = true;
}
if (checkpoint_.index_persistence_callback) {
// Notify the host that the index checkpoint has completed.
checkpoint_.index_persistence_callback(Status::Ok);
}
break;
////
case Phase::REST:
// PERSISTENCE_CALLBACK -> REST or INDEX_CHKPT -> REST
if (next_state.action != Action::CheckpointIndex) {
// The checkpoint is done; we can reset the contexts now. (Have to reset contexts before
// another checkpoint can be started.)
checkpoint_.CheckpointDone();
// Free checkpoint locks!
checkpoint_locks_.Free();
// Checkpoint is done--no more work for threads to do.
system_state_.store(SystemState{Action::None, Phase::REST, next_state.version});
} else {
// Get an overestimate for the ofb's tail, after we've finished fuzzy-checkpointing the
// ofb. (Ensures that recovery won't accidentally reallocate from the ofb.)
checkpoint_.index_metadata.ofb_count =
overflow_buckets_allocator_[resize_info_.version].count();
// Write index meta data on disk
if (WriteIndexMetadata() != Status::Ok) {
checkpoint_.failed = true;
}
auto index_persistence_callback = checkpoint_.index_persistence_callback;
// The checkpoint is done; we can reset the contexts now. (Have to reset contexts before
// another checkpoint can be started.)
checkpoint_.CheckpointDone();
// Checkpoint is done--no more work for threads to do.
system_state_.store(SystemState{Action::None, Phase::REST, next_state.version});
if (index_persistence_callback) {
// Notify the host that the index checkpoint has completed.
index_persistence_callback(Status::Ok);
}
}
break;
这个状态机太复杂,得花个图分析一下
状态机流转的途中进行WriteIndexMetadata来写入indexmeta,直接把二进制写进去
文件处理
FileSystemDisk
核心在file_t aka FileSystemFile
这里的handler_t是
#ifdef _WIN32
typedef FASTER::environment::ThreadPoolIoHandler handler_t;
#else
typedef FASTER::environment::QueueIoHandler handler_t;
#endif
真正的文件操作封装在这里,linux使用aio写的
对于文件分段管理,具体有FileSystemSegmentBundle和FileSystemSegmentedFile
hashtable
InternalHashTable
就是个bucket数组,还有一些记录信息
uint64_t size_;
HashBucket* buckets_;
/// State for ongoing checkpoint/recovery.
disk_t* disk_;
file_t file_;
hashbucket
用到了和address相同的对齐技巧
核心是bucket,bucket也是和cacheline对齐的
struct alignas(Constants::kCacheLineBytes) HashBucket {
/// Number of entries per bucket (excluding overflow entry).
static constexpr uint32_t kNumEntries = 7;
/// The entries.
AtomicHashBucketEntry entries[kNumEntries];
/// Overflow entry points to next overflow bucket, if any.
AtomicHashBucketOverflowEntry overflow_entry;
};
static_assert(sizeof(HashBucket) == Constants::kCacheLineBytes,
"sizeof(HashBucket) != Constants::kCacheLineBytes");
HashBucketOverflowEntry只有个address_
union {
struct {
uint64_t address_ : 48; // corresponds to logical address
uint64_t unused_ : 16;
};
uint64_t control_;
};
HashBucketEntry长这样
union {
struct {
uint64_t address_ : 48; // corresponds to logical address一般指针只用到48位
uint64_t tag_ : 14; //用来保存hash,类似cuckoohash,防撞
uint64_t reserved_ : 1;
uint64_t tentative_ : 1; //如果是1,说明在外面
};
uint64_t control_;
};
注意一个hashbucket有七个HashBucketEntry,这七个是相同的hash,如何判断在哪个bucketEntry?用tag
TODO: tag的生成逻辑? 目前来看就是hash.tag
如果有tentative标记,说明重复,正在写,重新分配通过BucketOverflowEntry指向外面的entry
MallocFixedPageSize
结构是这样的
/// Alignment at which each page is allocated.
uint64_t alignment_;
/// Array of all of the pages we've allocated.
std::atomic<FixedPageArray<T>*> page_array_;
/// How many elements we've allocated.
AtomicFixedPageAddress count_;
LightEpoch* epoch_;
/// State for ongoing checkpoint/recovery.
disk_t* disk_;
file_t file_;
std::atomic<uint64_t> pending_checkpoint_writes_;
std::atomic<uint64_t> pending_recover_reads_;
std::atomic<bool> checkpoint_pending_;
std::atomic<bool> checkpoint_failed_;
std::atomic<bool> recover_pending_;
std::atomic<bool> recover_failed_;
FreeList free_list_[Thread::kMaxNumThreads];
用disk.log().asignement初始化
Hlog PersistentMemoryMalloc
typedef FASTER::environment::QueueIoHandler handler_t; //文件的读写接口
typedef FASTER::device::FileSystemDisk<handler_t, 1073741824ull> disk_t; //FileSystemDisk持有真正的文件,所有记录
typedef PersistentMemoryMalloc<disk_t> hlog_t;
hlog构成
log_file_t* file;
// Read buffer pool
NativeSectorAlignedBufferPool read_buffer_pool;
NativeSectorAlignedBufferPool io_buffer_pool;
/// Every address < ReadOnlyAddress is read-only.
AtomicAddress read_only_address;
/// The minimum ReadOnlyAddress that every thread has seen.
AtomicAddress safe_read_only_address;
/// The circular buffer can drop any page < HeadAddress.page()--must read those pages from disk.
AtomicAddress head_address;
/// The minimum HeadPage that every thread has seen.
AtomicAddress safe_head_address;
AtomicAddress flushed_until_address;
/// The address of the true head of the log--everything before this address has been truncated
/// by garbage collection.
AtomicAddress begin_address;
uint32_t buffer_size_;
bool pre_allocate_log_;
/// -- the latest N pages should be mutable.
uint32_t num_mutable_pages_;
// Circular buffer definition
uint8_t** pages_;
// Array that indicates the status of each buffer page
FullPageStatus* page_status_;
// Global address of the current tail (next element to be allocated from the circular buffer)
AtomicPageOffset tail_page_offset_;
重点关注这几个address
buffer_size_ = static_cast
num_mutable_pages_要大于2 kNumHeadPages是4,在hlog开头
每一个page都是有FullPageStatus来描述,这里有个状态机驱动FlushCloseStatus,默认FlushStatus::Flushed, CloseStatus::Open
/// Pack flush- and close-status into a single 16-bit value.
/// State transitions are:
/// { Flushed, Closed } (default state)
/// --> { InProgress, Open } (when issuing the flush to disk)
/// --> either { . , Closed} (when moving the head address forward)
/// or { Flushed, . } (when the flush completes).
Hybrid log可以当成circular buffer,通过page状态来刷新推进
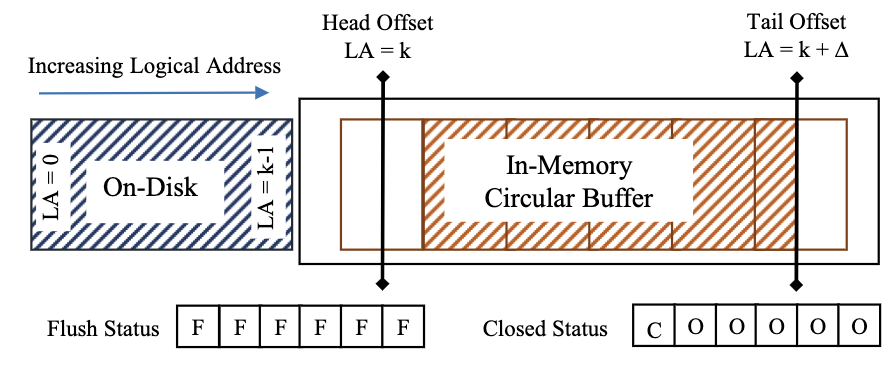
环形缓冲管理
我们需要使用无锁的方式将环形缓冲的数据刷盘,因此这里维护2个状态数组:
flush-status数组:追踪该页是否已经刷入磁盘closed-status数组:追踪该页是否可以清理以重用当日志尾进入新页$p+1$时,调用
BumpEpoch(Action),动作为“发起异步请求,将页$p$刷盘”。当刷盘完成后,设置该页的flush-status为flushed。由于HEAD偏移量跨越页边界时,会调用
Refresh,因此可以保证前页$p$已经完成,刷盘是安全的。当日志尾不断增加时,我们需要将环形缓冲头移除,以便于日志尾重用。当日志头需要往前时,先将头偏移量递增,然后调用
BumpEpoch(Action),动作为“设置该页的closed-status为closed”。当该
epoch安全时,所有线程都会看到头偏移量递增(多个线程肯定调用了Refresh,drain-list回调被触发),就不会访问旧页了。注意,在递增HEAD偏移量时,必须保证移除的页已经完成刷盘。
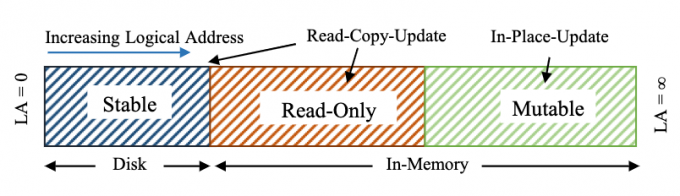
hlog空间设计

Hybrid Log地址空间分为3个部分:
- stable region:位于磁盘
- read-only region:位于内存,这个区域的键值对是只读的,即不能in-place更新,而使用RCU(读取-拷贝-修改,然后追加到mutable region)
- mutable region:位于内存,这个区域的键值对可以in-place更新
Hybrid Log地址空间使用3个偏移量管理:
- 尾偏移量、头偏移量:
- 只读偏移量:位于尾偏移量和头偏移量之间,分割read-only region和mutable region
- 和头偏移量类似,它和尾偏移量也保持大致相等的滞后,更新也在尾偏移量跨越页边界时进行
- 只读偏移量往前时,其后面的数据可以刷盘,刷盘完毕后即可从环形缓冲中移除,管理方式和5.2.所述的类似
- 只读偏移量充当了刷盘点,只读区域是可以刷盘的,但该区域数据存在时,还是能充当一个二级缓存
地址关系
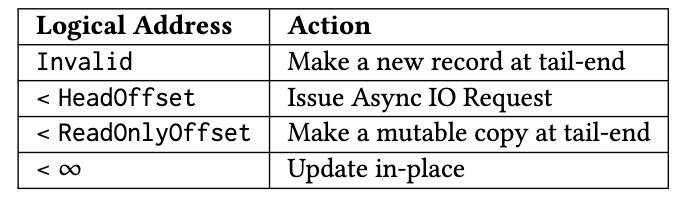
考虑一个mutation区域的record变成readonly,在两个线程视角不同的场景
丢数据
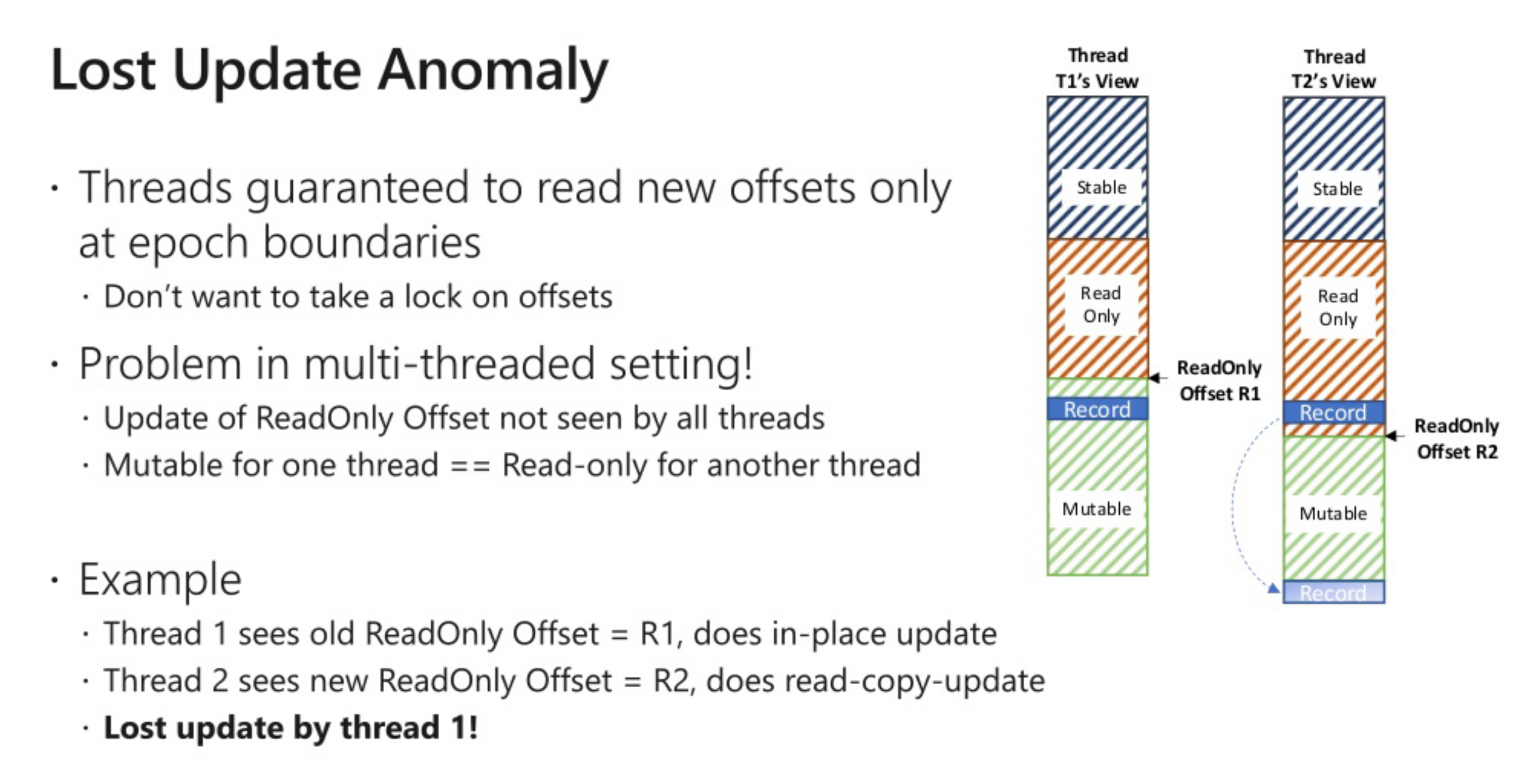
引入fuzzy region
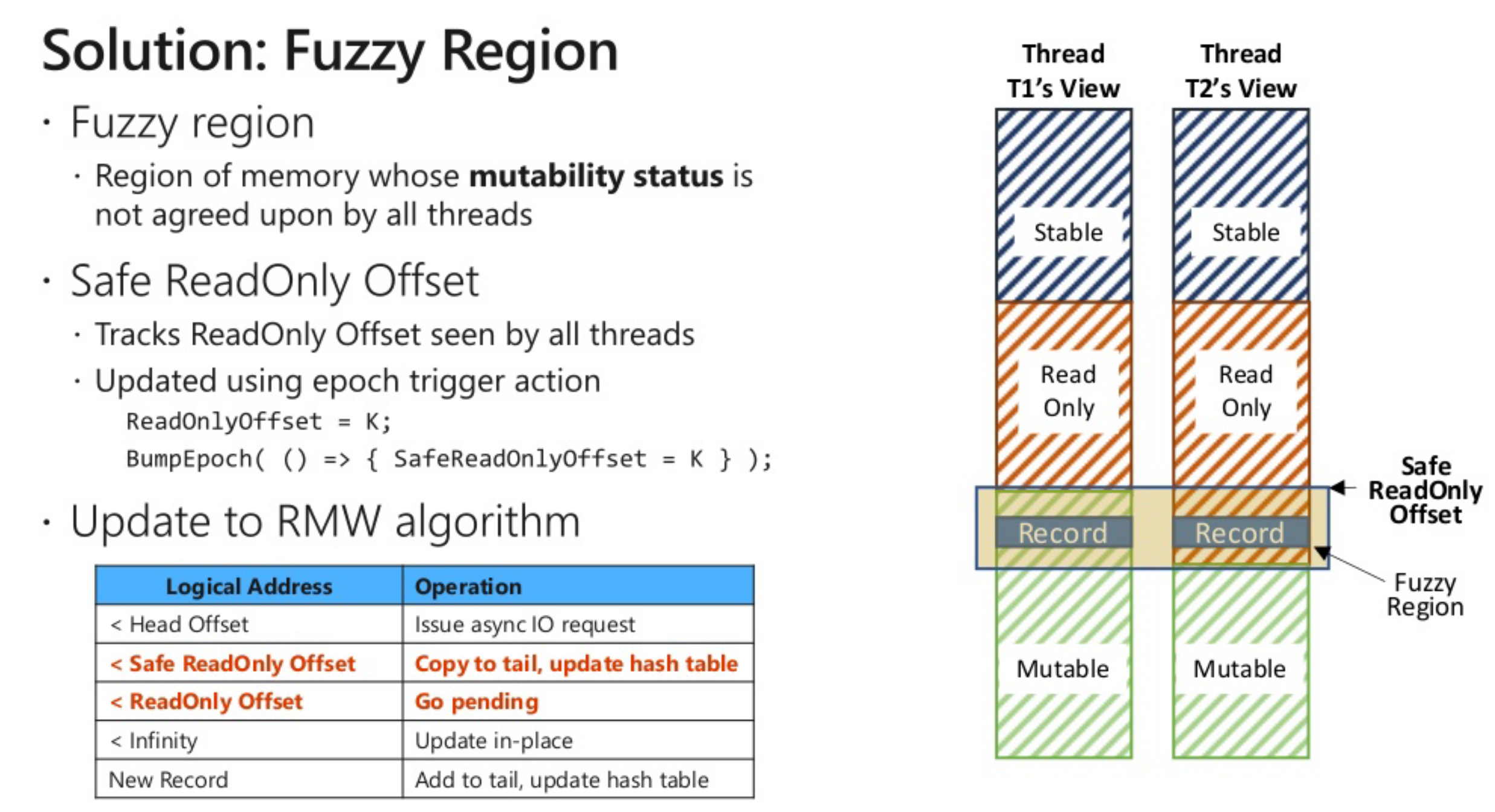
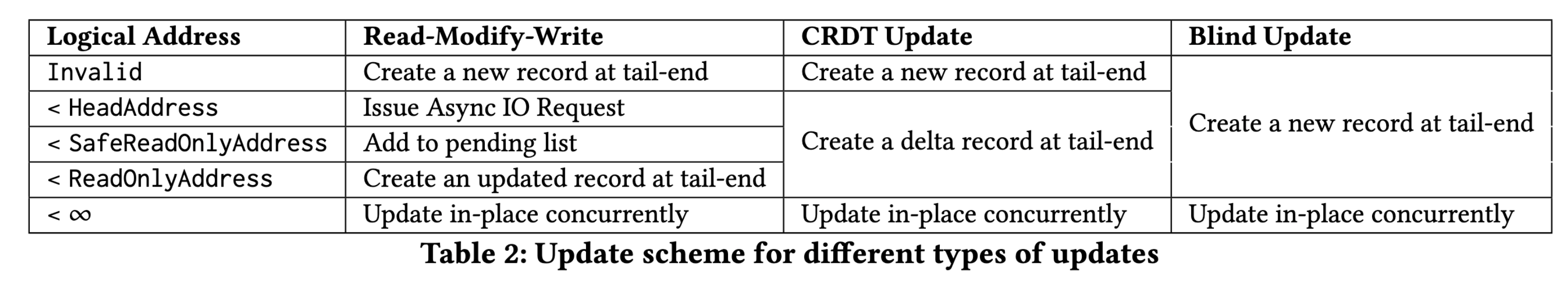
| 区域 | 更新方式 | 地址范围 |
|---|---|---|
| stable | 拷贝更新(read copy update) | [begin, head] |
| immutable | 拷贝更新(read copy update) | [head, safe read only] |
| fuzzy region | 排队竞争区域 | [safe read only, read only] |
| mutable | 就地更新(inplace update) | [read only, tail] |
// (Note that address will be Address::kInvalidAddress, if the atomic_entry was created.)
Address address = expected_entry.address();
Address begin_address = hlog.begin_address.load();
Address head_address = hlog.head_address.load();
Address read_only_address = hlog.read_only_address.load();
Address safe_read_only_address = hlog.safe_read_only_address.load();
Recover->RestoreHybridLog->RecoveryReset/hlog ctor中构造
hlog.head_address 不推进
read_only_address不推进
template <class K, class V, class D>
inline Address FasterKv<K, V, D>::BlockAllocate(uint32_t record_size) {
uint32_t page;
Address retval = hlog.Allocate(record_size, page);
while (retval < hlog.read_only_address.load()) {
Refresh();
// Don't overrun the hlog's tail offset.
bool page_closed = (retval == Address::kInvalidAddress);
while (page_closed) {
page_closed = !hlog.NewPage(page);
// printf("###page:%lld status:%d for size:%lld\n", page, page_closed, record_size);
Refresh();
}
retval = hlog.Allocate(record_size, page);
}
return retval;
}
几个交互流程
- HandleSpecialPhases/SplitHashTableBuckets
- GlobalMoveToNextState
- AsyncFlushPagesToFile
- GlobalMoveToNextState
- NewPage
- PageAlignedShiftReadOnlyAddress
- MonotonicUpdate
- BumpCurrentEpoch
- OnPagesMarkedReadOnly
- AsyncFlushPages
- OnPagesMarkedReadOnly
- PageAlignedShiftReadOnlyAddress
pageoffset
/// Use 41 bits for offset, which gives us approximately 2 PB of overflow space, for
/// Reserve().
union {
struct {
uint64_t offset_ : 64 - Address::kPageBits; //41
uint64_t page_ : Address::kPageBits; //23
};
uint64_t control_;
};
//
inline PageOffset Reserve(uint32_t num_slots) {
assert(num_slots <= Address::kMaxOffset);
PageOffset offset{ 0, num_slots };
return PageOffset{ control_.fetch_add(offset.control()) };
}
根据record大小算page,page的下一页用来具体的写
地址边界的变更时机
OnPagesClosed OnPagesClosed_Context
safe_read_only_address
//只在配置了fold_over_snapshot才调用
template <class D>
Address PersistentMemoryMalloc<D>::ShiftReadOnlyToTail() {
Address tail_address = GetTailAddress();
Address old_read_only_address;
if(MonotonicUpdate(read_only_address, tail_address, old_read_only_address)) {
OnPagesMarkedReadOnly_Context context{ this, tail_address, false };
IAsyncContext* context_copy;
Status result = context.DeepCopy(context_copy);
assert(result == Status::Ok);
epoch_->BumpCurrentEpoch(OnPagesMarkedReadOnly, context_copy);
}
return tail_address;
}
//调用PersistentMemoryMalloc<D>::NewPage(uint32_t old_page)生效
template <class D>
inline void PersistentMemoryMalloc<D>::PageAlignedShiftReadOnlyAddress(uint32_t tail_page) {
Address current_read_only_address = read_only_address.load();
if(tail_page <= num_mutable_pages_) {
// Desired read-only address is <= 0.
return;
}
Address desired_read_only_address{ tail_page - num_mutable_pages_, 0 };
Address old_read_only_address;
if(MonotonicUpdate(read_only_address, desired_read_only_address, old_read_only_address)) {
OnPagesMarkedReadOnly_Context context{ this, desired_read_only_address, false };
IAsyncContext* context_copy;
Status result = context.DeepCopy(context_copy);
assert(result == Status::Ok);
epoch_->BumpCurrentEpoch(OnPagesMarkedReadOnly, context_copy);
}
}
// 被上面的两个函数调用
template <class D>
void PersistentMemoryMalloc<D>::OnPagesMarkedReadOnly(IAsyncContext* ctxt) {
CallbackContext<OnPagesMarkedReadOnly_Context> context{ ctxt };
Address old_safe_read_only_address;
if(context->allocator->MonotonicUpdate(context->allocator->safe_read_only_address,
context->new_safe_read_only_address,
old_safe_read_only_address)) {
context->allocator->AsyncFlushPages(old_safe_read_only_address.page(),
context->new_safe_read_only_address);
}
}
safe_read_only_address
template <class D>
inline void PersistentMemoryMalloc<D>::PageAlignedShiftHeadAddress(uint32_t tail_page) {
//obtain local values of variables that can change
Address current_head_address = head_address.load();
Address current_flushed_until_address = flushed_until_address.load();
if(tail_page <= (buffer_size_ - kNumHeadPages)) {
// Desired head address is <= 0.
return;
}
Address desired_head_address{ tail_page - (buffer_size_ - kNumHeadPages), 0 };
if(current_flushed_until_address < desired_head_address) {
desired_head_address = Address{ current_flushed_until_address.page(), 0 };
}
Address old_head_address;
if(MonotonicUpdate(head_address, desired_head_address, old_head_address)) {
OnPagesClosed_Context context{ this, desired_head_address, false };
IAsyncContext* context_copy;
Status result = context.DeepCopy(context_copy);
assert(result == Status::Ok);
epoch_->BumpCurrentEpoch(OnPagesClosed, context_copy);
}
}
template <class D>
void PersistentMemoryMalloc<D>::OnPagesClosed(IAsyncContext* ctxt) {
CallbackContext<OnPagesClosed_Context> context{ ctxt };
Address old_safe_head_address;
if(context->allocator->MonotonicUpdate(context->allocator->safe_head_address,
context->new_safe_head_address,
old_safe_head_address)) {
for(uint32_t idx = old_safe_head_address.page(); idx < context->new_safe_head_address.page();
++idx) {
FlushCloseStatus old_status = context->allocator->PageStatus(idx).status.load();
FlushCloseStatus new_status;
do {
new_status = FlushCloseStatus{ old_status.flush, CloseStatus::Closed };
} while(!context->allocator->PageStatus(idx).status.compare_exchange_weak(old_status,
new_status));
if(old_status.flush == FlushStatus::Flushed) {
// We closed the page after it was flushed, so we are responsible for clearing and
// reopening it.
std::memset(context->allocator->Page(idx), 0, kPageSize);
context->allocator->PageStatus(idx).status.store(FlushStatus::Flushed, CloseStatus::Open);
}
}
Record
record对应recordinfo,以及真正的kv 注意,kv封装在一起
recordinfo结构
union {
struct {
uint64_t previous_address_ : 48;
uint64_t checkpoint_version : 13;
uint64_t invalid : 1;
uint64_t tombstone : 1;
uint64_t final_bit : 1;
};
uint64_t control_;
};
所有的字段排布都是pad_alignment的,保证8的整数倍
这里要求size和alignment都是2的幂
constexpr inline size_t pad_alignment(size_t size, size_t alignment) {
size_t max_padding = alignment - 1;
return (size + max_padding) & ~max_padding;
}
pad_alignment(sizeof(int64_t), alignof(std::string)); //8
这里引入一下对齐要求
每个对象类型都具有被称为对齐要求(alignment requirement)的性质,它是一个整数(类型为 std::size_t,总是 2 的幂),表示这个类型的不同对象所能分配放置的连续相邻地址之间的字节数。
可以用 alignof或 std::alignment_of 来查询类型的对齐要求。可以使用指针对齐函数 std::align 来获取某个缓冲区中经过适当对齐的指针,还可以使用 std::aligned_storage 来获取经过适当对齐的存储区。(C++11 起) 每个对象类型在该类型的所有对象上强制该类型的对齐要求;可以使用 alignas来要求更严格的对齐(更大的对齐要求)(C++11 起)。 为了使类中的所有非静态成员都符合对齐要求,会在一些成员后面插入一些填充。
用上alignof就要求保证最大对齐。这里也是cache 友好的一种手段
回到record record的size保证是8的整数倍, 在内存中
在磁盘中,省掉了value的padding
/// Size of a record to be created, in memory. (Includes padding, if any, after the value, so
/// that the next record stored in the log is properly aligned.)
static inline constexpr uint32_t size(uint32_t key_size, uint32_t value_size) {
return static_cast<uint32_t>(
// --plus Value size, all padded to Header alignment.
pad_alignment(value_size +
// --plus Key size, all padded to Value alignment.
pad_alignment(key_size +
// Header, padded to Key alignment.
pad_alignment(sizeof(RecordInfo), alignof(key_t)),
alignof(value_t)),
alignof(RecordInfo)));
/// Size of a record, on disk. (Excludes padding, if any, after the value.)
inline constexpr uint32_t disk_size() const {
return static_cast<uint32_t>(value().size() +
pad_alignment(key().size() +
// Header, padded to Key alignment.
pad_alignment(sizeof(RecordInfo), alignof(key_t)),
alignof(value_t)));
record和hlog的管理
Address new_address = BlockAllocate(record_size);
record_t *new_record = reinterpret_cast<record_t *>(hlog.Get(new_address));
...
inline const uint8_t *Get(Address address) const
{
return Page(address.page()) + address.offset();
}
Context
PersistentExecContext checkpoint信息
ExecutionContext 增加了phase状态
还有这几个成员
Phase phase;
/// Retry request contexts are stored inside the deque.
std::deque<IAsyncContext*> retry_requests;
/// Assign a unique ID to every I/O request.
uint64_t io_id;
/// For each pending I/O, maps io_id to the hash of the key being retrieved.
std::unordered_map<uint64_t, KeyHash> pending_ios;
/// The I/O completion thread hands the PendingContext back to the thread that issued the
/// request.
concurrent_queue<AsyncIOContext*> io_responses;
threadContext是ExecutionContext的封装,每个thread有两个executioncontext
class alignas(Constants::kCacheLineBytes) ThreadContext {
public:
ThreadContext()
: contexts_{}
, cur_{ 0 } {
}
inline const ExecutionContext& cur() const {
return contexts_[cur_];
}
inline ExecutionContext& cur() {
return contexts_[cur_];
}
inline const ExecutionContext& prev() const {
return contexts_[(cur_ + 1) % 2];
}
inline ExecutionContext& prev() {
return contexts_[(cur_ + 1) % 2];
}
inline void swap() {
cur_ = (cur_ + 1) % 2;
}
private:
ExecutionContext contexts_[2];
uint8_t cur_;
};
CallbackContext
IAsyncContext 封装CURD的context信息,特殊的context需要特别的方法,塞value之类的
PendingContext
pendingcontext信息
/// Caller context.
IAsyncContext* caller_context;
/// Caller callback.
AsyncCallback caller_callback;
/// Checkpoint version.
uint32_t version;
/// Checkpoint phase.
Phase phase;
/// Type of operation (Read, Upsert, RMW, etc.).
OperationType type;
/// Result of operation.
Status result;
/// Address of the record being read or modified.
Address address;
/// Hash table entry that (indirectly) leads to the record being read or modified.
HashBucketEntry entry;
状态机流转都是靠pendingcontext
AIO aio相关的使用
这里设计了一个context
塞了自己的context
struct IoCallbackContext {
IoCallbackContext(FileOperationType operation, int fd, size_t offset, uint32_t length,
uint8_t* buffer, core::IAsyncContext* context_, core::AsyncIOCallback callback_)
: caller_context{ context_ }
, callback{ callback_ } {
if(FileOperationType::Read == operation) {
::io_prep_pread(&this->parent_iocb, fd, buffer, length, offset);
} else {
::io_prep_pwrite(&this->parent_iocb, fd, buffer, length, offset);
}
::io_set_callback(&this->parent_iocb, IoCompletionCallback);
}
// WARNING: "parent_iocb" must be the first field in AioCallbackContext. This class is a C-style
// subclass of "struct iocb".
/// The iocb structure for Linux AIO.
struct iocb parent_iocb;
/// Caller callback context.
core::IAsyncContext* caller_context;
/// The caller's asynchronous callback function
core::AsyncIOCallback callback;
};
io_submit塞这个context,io_getevent拿数据
aio的主要问题是docker不能直接用 见这个SO
读
-
Read
-
InternalRead,三种状态,内存中,磁盘中,还是未找到
- 判断当前所处的cpr状态 如果不是REST,是其他状态,需要做一些标记动作HeavyEnter
- 根据context带来的key的hash来FindEntry
- 判定在那个version对应的hashtable中
- Action::GrowIndex控制version
- 如果internalHashTable中的HashBucketEntry不满足条件,那就找HashBucketEntry中对应的外部表
bucket = &overflow_buckets_allocator_[version].Get(entry.address());如果没位置了,继续放到外部
- 判定在那个version对应的hashtable中
- 判定Entry所在的address满足条件,拿到address,从hlog找到对应的record和查找的key进行比对
- 如果record->key不等于context带回来的key,走碰撞查询 TraceBackForKeyMatchCtxt, LRU的
-
HandleOperationStatus 读磁盘/重试
-
IssueAsyncIoRequest
-
AsyncGetFromDisk, 带上AsyncGetFromDiskCallback
-
Epoch protect状态处理
- disk.TryComplete();
- 进行io动作 io_getevents
- AsyncGetFromDiskCallback
- MinIoRequestSize 这里的size设定是sizeof(value_t) 假定t是定长,如果t不是定长呢?这个参数应该暴露出来
- 进行io动作 io_getevents
- std::this_thread::yield();
- epoch_.ProtectAndDrain();
- disk.TryComplete();
-
hlog->AsyncGetFromDisk
-
file->ReadAsync AIO, FileSystemSegmentedFile
-
OpenSegment, load或者保存对应的段
-
files->file(segment).ReadAsync(source % kSegmentSize, dest, length, callback, context); FileSystemSegmentBundle
-
FileSystemFile->ReadAsync
-
QueueFile::Read
- ScheduleOperation, IoCompletionCallback
- IoCallbackContext
- io_prep_pread
- io_set_callback 到这层 callback设置好
- io_submit 带着IoCallbackContext一起提交
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
case OperationStatus::RECORD_ON_DISK: if(thread_ctx().phase == Phase::PREPARE) { assert(pending_context.type == OperationType::Read || pending_context.type == OperationType::RMW); // Can I be marking an operation again and again? if(!checkpoint_locks_.get_lock(pending_context.get_key_hash()).try_lock_old()) { return PivotAndRetry(ctx, pending_context, async); } } return IssueAsyncIoRequest(ctx, pending_context, async); -
异步读磁盘的数据通过completepending拿到。异步。
context流动路径
asynccontex -> readcontext -> pending_read_context -> AsyncIOContext
读-> 改->写 基本和upsert一致
- Rmw
-
InternalRmw retry=false
- HeavyEnter
- FindOrCreateEntry
- TraceBackForKeyMatchCtxt
thread_ctx().phase == Phase::REST && address >= read_only_address开始正常写入,从hlog抠出recordpending_context.RmwAtomic(record)- 如果record不存在,已经被回收tombstone,需要走RCU更新 goto create_record
- CPR状态机处理
- PREPARE阶段,主要是处理旧的版本 CPR_SHIFT_DETECTED 条件
- 锁旧锁失败,说明当前肯定有更旧的,不然我们是最后一个旧的,就能锁上
latest_record_version > thread_ctx().version我们看到了比我们版本还要大的,需要调整version
- IN_PROGRESS阶段,锁新锁,失败重试,成功进入create_record流程
- WAIT_PENDING阶段,等待旧锁释放,进入create_record
- WAIT_FLUSH阶段,直接create_record
- PREPARE阶段,主要是处理旧的版本 CPR_SHIFT_DETECTED 条件
- Mutable region, RmwAtomic直接替换, 对比upsert没有这个流程,直接放到mutation
- fuzzy region pending_context.go_async
- create_record
if (old_record == nullptr || address < hlog.begin_address.load()) { pending_context.RmwInitial(new_record); } else if (address >= head_address) { pending_context.RmwCopy(old_record, new_record); } else { // The block we allocated for the new record caused the head address to advance beyond // the old record. Need to obtain the old record from disk. new_record->header.invalid = true; if (!retrying) { pending_context.go_async(phase, version, address, expected_entry); } else { pending_context.continue_async(address, expected_entry); } return OperationStatus::RECORD_ON_DISK; } HashBucketEntry updated_entry{new_address, hash.tag(), false}; if (atomic_entry->compare_exchange_strong(expected_entry, updated_entry)) { return OperationStatus::SUCCESS; } else { // CAS failed; try again. new_record->header.invalid = true; if (!retrying) { pending_context.go_async(phase, version, address, expected_entry); } else { pending_context.continue_async(address, expected_entry); } return OperationStatus::RETRY_NOW; } }
-
写
-
Upsert
-
InternalUpsert
- HeavyEnter
- FindOrCreateEntry,语义:如果是创建的,地址是Address::kInvalidAddress
- FindTentativeEntry 找满足条件的找不到用free的,如果没有free的,用overflow_entry
- 语义: 返回bucketEntry,并且能判断是free的还是已经存在的
- 如果overflow_entry没用,就分配一个
overflow_buckets_allocator_[version].Allocate();address,根据这个address创建overflow_entry- 进行并发修改overflow_entry
- 如果成功就把allocate好的address对应的bucket返回
- 失败,回退,回收对应的address
- 进行并发修改overflow_entry
- 如果overflow_entry已经分配,那就直接返回对应的bucket
- 根据FindTentativeEntry判定,如果是free的,写tag, 标记tentative,并发写,写成功就清掉tentative,写失败
- HasConflictingEntry检查是否有相同tag,有,说明冲突,继续循环写
- FindTentativeEntry 找满足条件的找不到用free的,如果没有free的,用overflow_entry
- 判定Entry所在的address满足条件,拿到address,
- 如果大于head_address, 根据地址从hlog找到对应的record
- 如果record->key不等于context带回来的key,走碰撞查询 TraceBackForKeyMatchCtxt, LRU的
- 如果大于head_address, 根据地址从hlog找到对应的record
thread_ctx().phase == Phase::REST && address >= read_only_address开始正常写入,从hlog抠出recordpending_context.PutAtomic(record)- 如果record不存在,已经被回收tombstone,需要走RCU更新 goto create_record
- CPR状态机处理
- PREPARE阶段,主要是处理旧的版本 CPR_SHIFT_DETECTED 条件
- 锁旧锁失败,说明当前肯定有更旧的,不然我们是最后一个旧的,就能锁上
latest_record_version > thread_ctx().version我们看到了比我们版本还要大的,需要调整version
- IN_PROGRESS阶段,锁新锁,失败重试,成功进入create_record流程
- WAIT_PENDING阶段,等待旧锁释放,进入create_record
- WAIT_FLUSH阶段,直接create_record
- PREPARE阶段,主要是处理旧的版本 CPR_SHIFT_DETECTED 条件
- Mutable region, PutAtomic
- create_record
- FasterKv<K, V, D>::BlockAllocate
- PersistentMemoryMalloc
::Allocate - retval < hlog.read_only_address.load() ? refresh更新epoch Newpage 继续Allocate
uint32_t record_size = record_t::size(pending_context.key_size(), pending_context.value_size()); Address new_address = BlockAllocate(record_size); record_t* record = reinterpret_cast<record_t*>(hlog.Get(new_address)); new(record) record_t{ RecordInfo{ static_cast<uint16_t>(thread_ctx().version), true, false, false, expected_entry.address() } }; pending_context.write_deep_key_at(const_cast<key_t*>(&record->key())); pending_context.Put(record); HashBucketEntry updated_entry{ new_address, hash.tag(), false }; if(atomic_entry->compare_exchange_strong(expected_entry, updated_entry)) { // Installed the new record in the hash table. return OperationStatus::SUCCESS; } else { // Try again. record->header.invalid = true; return InternalUpsert(pending_context); }
-
template <class K, class V, class D>
inline Address FasterKv<K, V, D>::BlockAllocate(uint32_t record_size) {
uint32_t page;
Address retval = hlog.Allocate(record_size, page);
while(retval < hlog.read_only_address.load()) {
Refresh();
// Don't overrun the hlog's tail offset.
bool page_closed = (retval == Address::kInvalidAddress);
while(page_closed) {
page_closed = !hlog.NewPage(page);
Refresh();
}
retval = hlog.Allocate(record_size, page);
}
return retval;
}
template <class D>
inline Address PersistentMemoryMalloc<D>::Allocate(uint32_t num_slots, uint32_t& closed_page) {
closed_page = UINT32_MAX;
PageOffset page_offset = tail_page_offset_.Reserve(num_slots);
if(page_offset.offset() + num_slots > kPageSize) {
// The current page is full. The caller should Refresh() the epoch and wait until
// NewPage() is successful before trying to Allocate() again.
closed_page = page_offset.page();
return Address::kInvalidAddress;
} else {
assert(Page(page_offset.page()));
return static_cast<Address>(page_offset);
}
}
-
操作失败的HandleOperationStatus 状态机
- CPR_SHIFT_DETECTED PivotAndRetry,推进版本号
- Refresh
- epoch_.ProtectAndDrain
- HandleSpecialPhases
- Action phase双层状态机 所有东西都混在一起了。难受
- Refresh
- CPR_SHIFT_DETECTED PivotAndRetry,推进版本号
如果hash碰撞率高,可能会有bug
AsyncIOContext
对于异步的请求处理,会涉及到AsyncIOContext把所有的状态记录下来
void *faster;
Address address;
IAsyncContext *caller_context;
concurrent_queue<AsyncIOContext *> *thread_io_responses;
uint64_t io_id;
SectorAlignedMemory record;
pthread_t pid;
其中record来保存各种记录,thread_io_responses来记录各种pending请求
SectorAlignedMemory
内部结构
private:
uint8_t* buffer_;
public:
uint32_t valid_offset;
uint32_t required_bytes;
uint32_t available_bytes;
private:
uint32_t level_;
NativeSectorAlignedBufferPool* pool_;
buffer给外部使用,pool分配内存, pool Get拿到SectorAlignedMemory
这个pool是hlog(PersistentMemoryMalloc)内部有的,从外部传进来
// Read buffer pool
NativeSectorAlignedBufferPool read_buffer_pool;
NativeSectorAlignedBufferPool io_buffer_pool;
NativeSectorAlignedBufferPool::Get
这个内存池设计的挺有意思,和那个lss_allocator差不多。思想是 log structure memory allocator
inline SectorAlignedMemory NativeSectorAlignedBufferPool::Get(uint32_t numRecords) {
// How many sectors do we need?
uint32_t sectors_required = (numRecords * record_size_ + sector_size_ - 1) / sector_size_;
uint32_t level = Level(sectors_required);
uint8_t* buffer;
if(queue_[level].try_pop(buffer)) {
return SectorAlignedMemory{ buffer, level, this };
} else {
uint8_t* buffer = reinterpret_cast<uint8_t*>(aligned_alloc(sector_size_,
sector_size_ * (1 << level)));
return SectorAlignedMemory{ buffer, level, this };
}
}
queue是个数组,每个level有内存块,pop出来,没有就alloc出来,后面回收在放到queue里
具体的使用
template <class D>
inline void PersistentMemoryMalloc<D>::AsyncGetFromDisk(Address address, uint32_t num_records, AsyncIOCallback callback,
AsyncIOContext &context)
{
uint64_t begin_read, end_read;
uint32_t offset, length;
GetFileReadBoundaries(address, num_records, begin_read, end_read, offset, length);
context.record = read_buffer_pool.Get(length);
context.record.valid_offset = offset;
context.record.available_bytes = length - offset;
context.record.required_bytes = num_records;
file->ReadAsync(begin_read, context.record.buffer(), length, callback, context);
}
scan
scan就是扫描hlog文件。这个扫描是有bug的。并发写入中,hlog是可能存在空洞的。而空洞的判定得8字节跳过。
没有magic header来判定真正有效的数据。所以基于scan来做数据去重,坑非常多。我已经搞出两个线上问题了。这个傻逼玩意
TTL
hashtable如何支持ttl?
segcache的做法是单独搞一个ttl的表
key级别的ttl
当前delete的动作是加一个tombstone标签
ttl可以敷用这个标签,如果过期,直接标记即可
如果记录时间戳,没有多余的空间来放在key中,只能放在record中,get的时候解出来时间戳然后校验,不满足就标记
整体级别的ttl
hlog是追加写,根据一个系统级别的时间戳,直接把hlog截断,比如三天后数据失效
Compact
FasterKv<K, V, D>::Compact(uint64_t untilAddress)- 初始化一个tempkv,大小就用给定地址到hlog开头到差值到二倍,或者kPageSize *8
- 遍历 源kv的hlog
ScanIterator<faster_t> iter(&hlog, Buffering::DOUBLE_PAGE, begin, Address(untilAddress), &disk);- r->header.tombstone tempKv.Delete /tempKv.Upsert
- 定期Refresh tempkv和源kv都是
- LogScanForValidity safe_read_only_address可能在变化中,所以要把这个地址下的可变key都删掉,返回最新的safe_read_only_address 这时候的tempkv有的是所有的不变的key-value
- 遍历 tempkv的hlog
ScanIterator<faster_t> iter2(&tempKv.hlog, Buffering::DOUBLE_PAGE, tempKv.hlog.begin_address.load(), tempKv.hlog.GetTailAddress(), &tempKv.disk);- 没被删除且满足
!ContainsKeyInMemory(r->key(), upto))才upsert, 这里的upto是最新的safe_read_only_address,也就是说,key得在不变区- 源kv上Upsert CompactionUpsert,把最新的kv搞过来, 放到可变区mutation
- 定期refresh , tempkv和源kv都是
- 如果safe_read_only_address变了,还要LogScanForValidity一次
- 没被删除且满足
能看到,这个流程就是把以前stable的数据重新搬到mutation区域,且已知compact开始的地址,何时真正的删除文件?
bool FasterKv<K, V, D>::ShiftBeginAddress(Address address, GcState::truncate_callback_t tcb,GcState::complete_callback_t ccb)- SystemState判定
hlog.begin_address.store(address);设定开头- 通知epoch
epoch_.ResetPhaseFinished(); - 开始gc
gc_.Initialize(truncate_callback, complete_callback, num_chunks); - systemstate设定
这里也没有处理文件,真正处理文件在状态机
GlobalMoveToNextState...
case Phase::GC_IN_PROGRESS:
// GC_IO_PENDING -> GC_IN_PROGRESS
// Tell the disk to truncate the log.
hlog.Truncate(gc_.truncate_callback);
break;
HandleSpecialPhases...
case Action::GC:
switch (current_state.phase) {
case Phase::GC_IO_PENDING:
// Handle REST -> GC_IO_PENDING and GC_IO_PENDING -> GC_IO_PENDING.
if (previous_state.phase == Phase::REST) {
assert(prev_thread_ctx().retry_requests.empty());
assert(prev_thread_ctx().pending_ios.empty());
assert(prev_thread_ctx().io_responses.empty());
// Get a new thread context; keep track of the old one as "previous."
thread_contexts_[Thread::id()].swap();
// initialize a new local context
thread_ctx().Initialize(Phase::GC_IO_PENDING, current_state.version,
prev_thread_ctx().guid, prev_thread_ctx().serial_num);
}
// See if the old thread context has completed its pending I/Os.
if (!epoch_.HasThreadFinishedPhase(Phase::GC_IO_PENDING)) {
if (prev_thread_ctx().pending_ios.empty() &&
prev_thread_ctx().retry_requests.empty()) {
// Thread ack that it has completed its pending I/Os.
if (epoch_.FinishThreadPhase(Phase::GC_IO_PENDING)) {
GlobalMoveToNextState(current_state);
}
}
}
break;
case Phase::GC_IN_PROGRESS:
// Handle GC_IO_PENDING -> GC_IN_PROGRESS and GC_IN_PROGRESS -> GC_IN_PROGRESS.
if (!epoch_.HasThreadFinishedPhase(Phase::GC_IN_PROGRESS)) {
if (!CleanHashTableBuckets()) {
// No more buckets for this thread to clean; thread has finished GC.
thread_ctx().phase = Phase::REST;
// Thread ack that it has finished GC.
if (epoch_.FinishThreadPhase(Phase::GC_IN_PROGRESS)) {
GlobalMoveToNextState(current_state);
}
}
}
break;
default:
assert(false); // not reached
break;
}
break;
PersistentMemoryMalloc<D>::TruncateFileSystemSegmentedFile::Truncate
void Truncate(uint64_t new_begin_offset, core::GcState::truncate_callback_t callback) {
uint64_t new_begin_segment = new_begin_offset / kSegmentSize;
begin_segment_ = new_begin_segment;
TruncateSegments(new_begin_segment, callback);
}
具体删除文件在TruncateSegments里,通过epoch_->BumpCurrentEpoch(callback, context_copy);去删除文件
auto callback = [](core::IAsyncContext* ctxt) {
core::CallbackContext<Context> context{ ctxt };
for(uint64_t idx = context->files->begin_segment; idx < context->new_begin_segment; ++idx) {
file_t& file = context->files->file(idx);
file.Close(); //::close
file.Delete(); //::remove
}
std::free(context->files);
if(context->caller_callback) {
context->caller_callback(context->new_begin_segment * kSegmentSize);
}
};
方案缺陷
compact的粒度是用户控制的,且默认是整个搬到mutation区域。可以针对这个控制粒度做优化,比如以文件为单位,文件中50%以上是delete的没用的key,才选出来做compact
这就需要一个compact range的功能。理论上是可以做的。但是这样做,hlog就相当于出现了地址空洞,需要有断层部分的管理,以及CURD动作访问到空洞的维护动作。
或者如果有文件出现了50%以上的删除的key,就从这个文件开始gc。这样比原有的compact方案细化了一点
该方法会重新生成 个db,导致大量分配内存
测了个一亿key,kv大概300,体积13G,机器是8u16G,compact途中内存爆增 BlockAllocate分配失败,但是faster是不会处理malloc失败的,后面memcpy直接越界segfault
堆栈列出来方便后面检索
#0 0x00007f9103abda54 in __memset_sse2 () from /lib64/libc.so.6
#1 0x000000000026b4c1 in FASTER::core::PersistentMemoryMalloc<FASTER::device::FileSystemDisk<FASTER::environment::QueueIoHandler, 1073741824ul> >::AllocatePage (this=this@entry=0x7f90e59ce0d8, index=<optimized out>, index@entry=356) at /data/FASTER/cc/src/core/persistent_memory_malloc.h:647
#2 0x000000000027984b in FASTER::core::PersistentMemoryMalloc<FASTER::device::FileSystemDisk<FASTER::environment::QueueIoHandler, 1073741824ul> >::NewPage (
old_page=354, this=0x7f90e59ce0d8) at /data/FASTER/cc/src/core/persistent_memory_malloc.h:707
#3 FASTER::core::FasterKv<util::StringKey, util::StringValue, FASTER::device::FileSystemDisk<FASTER::environment::QueueIoHandler, 1073741824ul> >::BlockAllocate (this=this@entry=0x7f90e59cc700, record_size=<optimized out>) at /data/FASTER/cc/src/core/faster.h:1781
#4 0x000000000027bb95 in FASTER::core::FasterKv<util::StringKey, util::StringValue, FASTER::device::FileSystemDisk<FASTER::environment::QueueIoHandler, 1073741824ul> >::InternalUpsert<FASTER::core::PendingUpsertContext<FASTER::core::CompactionUpsert<util::StringKey, util::StringValue> > > (
this=this@entry=0x7f90e59cc700, pending_context=...) at /data/FASTER/cc/src/core/faster.h:1215
#5 0x0000000000285d18 in FASTER::core::FasterKv<util::StringKey, util::StringValue, FASTER::device::FileSystemDisk<FASTER::environment::QueueIoHandler, 1073741824ul> >::Upsert<FASTER::core::CompactionUpsert<util::StringKey, util::StringValue> > (monotonic_serial_num=0,
callback=0x263d30 <FASTER::core::FasterKv<util::StringKey, util::StringValue, FASTER::device::FileSystemDisk<FASTER::environment::QueueIoHandler, 1073741824ul> >::Compact(unsigned long)::{lambda(FASTER::core::IAsyncContext*, FASTER::core::Status)#1}::_FUN(FASTER::core::IAsyncContext*, FASTER::core::Status)>,
context=..., this=0x7f90e59cc700) at /data/FASTER/cc/src/core/faster.h:695
#6 FASTER::core::FasterKv<util::StringKey, util::StringValue, FASTER::device::FileSystemDisk<FASTER::environment::QueueIoHandler, 1073741824ul> >::Compact
CompactWithLookup
在cc-lmhc分支,加了一个新的compact方法 CompactWithLookup
bool FasterKv<K, V, D>::CompactWithLookup (uint64_t until_address, bool shift_begin_address, int n_threads)
支持判定是否截断,支持多线程
主要修改点
引入状态 OperationType::Exists这个状态,嵌入PendingExistsContext,
pending状态的清理
使用者主动调用CompletePending/主动调用stopSession,会触发CompleteIoPendingRequests
然后抓到Exists状态,调用InternalContinuePendingExists,这个判断很简单,只要是addr合法,就SUCCESS,否则NOT_FOUND
注意,completepending内部有malloc,要注意重入问题, 如果由信号触发completepending,会死锁
一个死锁堆栈供参考
#0 0x00007f220b1016ec in __lll_lock_wait_private () from /lib64/libc.so.6
#1 0x00007f220b07dba2 in _L_lock_16654 () from /lib64/libc.so.6
#2 0x00007f220b07a7e3 in malloc () from /lib64/libc.so.6
#3 0x00007f220bfa3938 in operator new(unsigned long) () from /lib64/libstdc++.so.6
#4 0x000000000026d1ff in __gnu_cxx::new_allocator<FASTER::core::CompactionPendingRecordEntry<util::StringKey, util::StringValue> >::allocate (this=0x7ffee4d54480, __n=16) at /usr/include/c++/7/ext/new_allocator.h:111
#5 std::allocator_traits<std::allocator<FASTER::core::CompactionPendingRecordEntry<util::StringKey, util::StringValue> > >::allocate (__a=..., __n=16) at /usr/include/c++/7/bits/alloc_traits.h:436
#6 std::_Deque_base<FASTER::core::CompactionPendingRecordEntry<util::StringKey, util::StringValue>, std::allocator<FASTER::core::CompactionPendingRecordEntry<util::StringKey, util::StringValue> > >::_M_allocate_node (this=0x7ffee4d54480) at /usr/include/c++/7/bits/stl_deque.h:602
#7 std::deque<FASTER::core::CompactionPendingRecordEntry<util::StringKey, util::StringValue>, std::allocator<FASTER::core::CompactionPendingRecordEntry<util::StringKey, util::StringValue> > >::_M_push_back_aux<FASTER::core::CompactionPendingRecordEntry<util::StringKey, util::StringValue> const&> (this=0x7ffee4d54480) at /usr/include/c++/7/bits/deque.tcc:487
#8 0x000000000026d481 in std::deque<FASTER::core::CompactionPendingRecordEntry<util::StringKey, util::StringValue>, std::allocator<FASTER::core::CompactionPendingRecordEntry<util::StringKey, util::StringValue> > >::push_back (__x=..., this=<optimized out>) at /usr/include/c++/7/bits/stl_deque.h:1552
#9 FASTER::core::FasterKv<util::StringKey, util::StringValue, FASTER::device::FileSystemDisk<FASTER::environment::QueueIoHandler, 1073741824ul> >::InternalCompact<FASTER::core::FasterKv<util::StringKey, util::StringValue, FASTER::device::FileSystemDisk<FASTER::environment::QueueIoHandler, 1073741824ul> > >(FASTER::core::CompactionThreadsContext<FASTER::core::FasterKv<util::StringKey, util::StringValue, FASTER::device::FileSystemDisk<FASTER::environment::QueueIoHandler, 1073741824ul> > >*, int)::{lambda(FASTER::core::IAsyncContext*, FASTER::core::Status)#1}::operator()(FASTER::core::IAsyncContext*, FASTER::core::Status) const (__closure=<optimized out>, ctxt=0x55d720, result=<optimized out>) at /data/rimos_faster/cc/src/core/faster.h:3628
#10 0x000000000027aed3 in FASTER::core::FasterKv<util::StringKey, util::StringValue, FASTER::device::FileSystemDisk<FASTER::environment::QueueIoHandler, 1073741824ul> >::CompleteIoPendingRequests (this=this@entry=0x508840, context=...) at /data/rimos_faster/cc/src/core/faster.h:825
#11 0x000000000025da8d in FASTER::core::FasterKv<util::StringKey, util::StringValue, FASTER::device::FileSystemDisk<FASTER::environment::QueueIoHandler, 1073741824ul> >::CompletePending (this=0x508840, wait=false) at /data/rimos_faster/cc/src/core/faster.h:765
#12 0x00000000002810b8 in std::function<void (bool)>::operator()(bool) const (__args#0=<optimized out>, this=0x557e50) at /usr/include/c++/7/bits/std_function.h:706
社区版本的compact没有考虑hlog文件空洞的场景,使用可能会把数据写乱
另外遍历逻辑也有bug,没有真正的去读磁盘,导致遍历丢数据
这个项目的代码让我真实的体会到了社会的险恶,开源代码使用后果自负
主要路径
先遍历
LogPageIterator<faster_t> iter(&hlog, hlog.begin_address.load(),
Address(until_address), &disk);
CompactionThreadsContext<faster_t> threads_context{ &iter, n_threads-1 };
// Spawn the threads first
for (int idx = 0; idx < n_threads - 1; ++idx) {
threads.emplace_back(&FasterKv<K, V, D>::InternalCompact<faster_t>,
this, &threads_context, idx);
}
InternalCompact(&threads_context, -1); // participate in the compaction
-
FasterKv<K, V, D>::InternalCompact(CompactionThreadsContext<F>* ct_ctx, int thread_idx)- callback
CallbackContext<CompactionExists<K, V>> context(ctxt);,RecordExists用
typedef std::unordered_map<uint64_t, pending_record_entry_t> pending_records_info_t; typedef std::deque<pending_record_entry_t> pending_records_queue_t; pending_records_info_t pending_records_info; pending_records_queue_t pending_records_queue; auto callback = [](IAsyncContext* ctxt, Status result) { CallbackContext<CompactionExists<K, V>> context(ctxt); assert(result == Status::Ok || result == Status::NotFound); uint64_t address = context->record_address().control(); auto records_info = static_cast<pending_records_info_t*>(context->records_info()); auto records_queue = static_cast<pending_records_queue_t*>(context->records_queue()); if (result == Status::NotFound) { // retrieve record info auto record_info = records_info->find(address); assert(record_info != records_info->end()); // push record info to pending records queue records_queue->push_back(record_info->second); } // remove info for this record, since it has been processed records_info->erase(address); };- 死循环
- 有retry_records_queue先retry
- 遍历page
LogPageCollection<F>::GetNextRecord(record_address)- LogPage.GetNext current_addr
- 拿不到record,判定当前的pending是否处理完,走
goto complete_pending- Refresh() , 拿新page
CompactionThreadsContext.iter->GetNextPage(pages) - 循环GetNextPageAddress 遍历begin_adderss, untiladdress
- 步进Address desired(current_addr.page() + 1, 0);
- 遍历成功 IssueReadAsyncRequest,否则结束
- Refresh() , 拿新page
- 拿到record,是被删的,tombstone,跳过, 走
goto complete_pending - 正常场景,构造record_info ` record_info = new (pending_record_entry) pending_record_entry_t(record, record_address, expected_entry, record_address + 1);`
- record_info放进pending_records_info,放进 CompactionExists<K, V> context,走RecordExists,把CompactExistContext塞进pendingExistContext
- HeavyEnter
- FindEntry,和read一样,如果没有要放到pending queue里 这里的找不到,语义是地址变了的key,在后面的遍历里会遇到
- 找到,校验地址,判定在mutable fuzzy还是imm,imm就是not found,走copy to tail 这个能理解,怎么区分imm和找不到呢。这里的找不到,语义是地址变了的key,应该区分不出,这里是bug,必须能找到
- 在磁盘的话走go_async HandleOperationStatus
- IssueAsyncIoRequest
- AsyncGetFromDisk
- hlog.AsyncGetFromDisk
- GetFileReadBoundaries
- file->ReadAsync
- hlog.AsyncGetFromDisk
- AsyncGetFromDisk
- IssueAsyncIoRequest
- 如果是Pending,跳过,后面有complete_pending,其他场景,从pending_records_info删除
- 如果not found,放到pending_records_queue,后面走copy to tail
- record_info有可能是retry_records_queue new出来的,所以还要注意一下清理。这里用了placemanet new和new
- complete_pending
- CompletePending(false);/ std::this_thread::yield()
- 循环,遍历pending_records_queue
- ConditionalCopyToTail 实际上就是搬到mutable区域
- FindOrCreateEntry
- Pending,复制一份record_info,放到retry_records_queue (new出来的,注意)
- 如果队列都是空的,就完事儿了,break
- ConditionalCopyToTail 实际上就是搬到mutable区域
- CompletePending(true);,StopSession,done标记true
- callback
数据评估
基本的数据信息
HashBucket 设计的和kCacheLineBytes 一样,64字节
hlog的kPageSize 32M 2^25 bytes
overflow bucket的kPageSize 1M 2^20 bytes
主要内存占用
-
hashtable
InternalHashTable<disk_t> state_[2];外部指定table size - overflow buckets
MallocFixedPageSize<HashBucket, disk_t> overflow_buckets_allocator_[2]; - hlog
PersistentMemoryMalloc<disk_t>hlog的大小和log_mutable_fraction(0.9)可以由用户指定
这里逐个分析占用
hashtable
主要构成就是HashBucket* buckets_;其他的都是flag之类的信息
通过state_[0].Initialize(table_size, disk.log().alignment());初始化,table_size也是外部指定的,不能超过INT32_MAX
分配的大小就是size * 64, 这里用4M来算 4M* 64* 2 也就是512M
overflow buckets
array_t* page_array = array_t::Create(alignment, 2, nullptr);
page_array->AddPage(0);
page_array_.store(page_array, std::memory_order_release);
// Allocate the null pointer.
Allocate();
static FixedPageArray* Create(uint64_t alignment, uint64_t size, const array_t* old_array) {
void* buffer = std::malloc(sizeof(array_t) + size * sizeof(std::atomic<page_t*>));
return new(buffer) array_t{ alignment, size, old_array };
}
alignment默认4k
array_t是FixedPageArray<HashBucket>
Page_t是 FixedPage<HashBucket>内部是一个数组 T elements_[kPageSize]; 也就是64M
总占用也就是一个指针+ 一个page,这里只考虑page,64M,一共两个,也就是128M
page的个数是没有上限的,代码中没有处理page分配失败的场景
freelist
FreeList数组,一共kMaxNumThreads 96个,每个大都是std::deque<addr+epoch> 对齐cacheline 也就是64*96 6k可以忽略不计
关注每个entry实际占用
hlog
这里考虑log size 1G
log size必须是kpagesize的整数倍,所以用1G算,一共用32个page,其中,指定的log_mutable_fraction是0.9
immutable的存活时间?主要取决于什么时候去刷。这里没有rocksdb那种个数限制
最小内存
mutable最少2个,immutable最少kNumHeadPages=4个,所以这里log_mutable_fraction = 2/(4+2) = 0.4
最小内存是6*32M = 192M
如果设置了pre_allocate_log=true则分配制定大小而不是走最小的192M
我这里用valgrind抓了一个加载checkpoint数据的内存信息, table size 8M hlog1G
valgrind --tool=massif --pages-as-heap=yes --time-unit=B ./load_test
ms_print massif.out.5780 >massif.log
这里放一下日志
总占用764M fasterkv占704M hashtable 512M 8M * 64 + 192 基本一致
论文的性能测试
Hot-Ring
之前了解了阿里的这个FAST ‘20 - HotRing: A Hotspot-Aware In-Memory Key-Value Store,看了视频才知道这个工作是基于fasterkv之上的, 给热点key加了个chain hash
视频在这里https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NUmcE9BDvVE
他有一部分演讲的内容就是在介绍fasterkv的tag技巧
之前搜集的资料
- https://www.cnblogs.com/helloworldcode/p/13022166.html
- https://github.com/Focus5679/HotRing-simple-and-simple-demo
FishStore
FishStore是一个新的存储层:
-
支持灵活格式的数据
-
将快速解析和基于散列的子集索引结合,提供快速解析和抽取指定字段的能力
-
支持动态注册预测子集函数(PSF),允许用户获取所有满足给定PSF和值的记录
PSF:一个函数f:R→D
,基于给定的感兴趣的字段集合,将所有记录r∈R转换到值d∈D
基于PSF的索引效率高且扩展性好,并支持多种类型的查询(单点、联合、选择、前缀、预定义范围查询等)
FishStore的核心即PSF(Predicated Subset Function),它按照某些相似的特性,在逻辑上将记录进行分组,以供后面的检索。
参考信息
- https://github.com/microsoft/FASTER
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/111130238
- https://www.zhihu.com/question/291185867
- https://nan01ab.github.io/2019/05/FASTER.html
- https://microsoft.github.io/FASTER/docs/td-slides-videos/
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=68YBpitMrMI 咖喱味太重了,基本听不明白,不建议看
- 他还做了个CMU的演讲,讲的比上面这个十分钟的多一些 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4Y0oNFud-VA
- https://microsoft.github.io/FASTER/docs/td-research-papers/
- https://zh.cppreference.com/w/c/memory/aligned_alloc
void *aligned_alloc( size_t alignment, size_t size );
分配
size字节未初始化的存储空间,按照alignment指定对齐。size参数必须是alignment的整数倍。
- https://github.com/microsoft/FishStore 师出同门
- https://badrish.net/papers/fishstore-sigmod19.pdf
- 给faster加上io uring https://github.com/microsoft/FASTER/pull/387/files
- https://keys961.github.io/2020/07/05/%E8%AE%BA%E6%96%87%E9%98%85%E8%AF%BB-FASTER/
- https://keys961.github.io/2020/07/10/%E8%AE%BA%E6%96%87%E9%98%85%E8%AF%BB-FishStore/ 小伙的这两篇博客给了非常多的思路
