(译)用std::list的splice接口来实现LRU Cache
29 Nov 2020
|
|
原文 splice拼接
这是老考试题了,实现一个查O1 插入O1的LRU cache
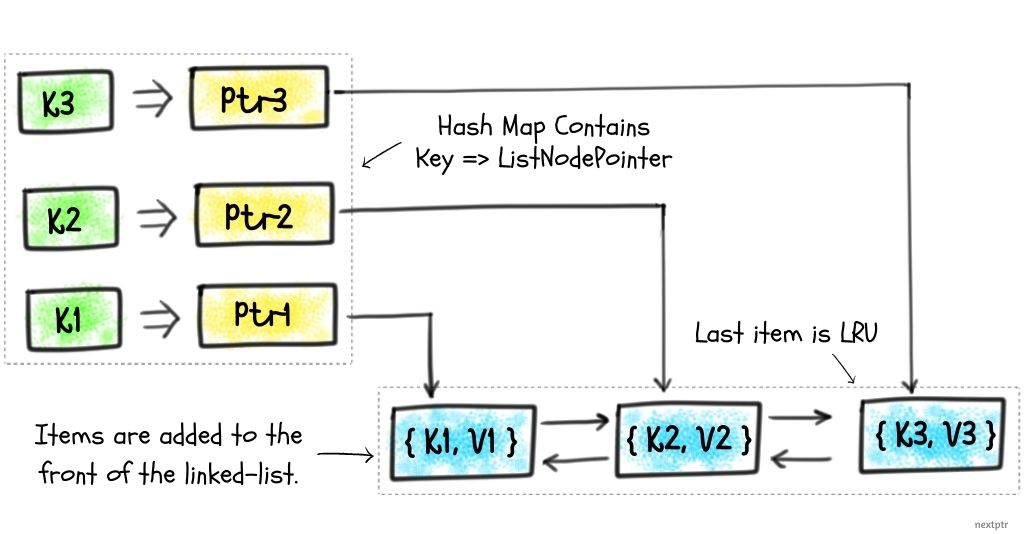
首先,要保证O1查找,必然需要一个hash表存key,可以用unordered_map unordered_map性能表现特别差,暂且不讨论
然后,保证O1插入 hash表/链表页满足条件
但是,要实现LRU排序,必须要引入list来维护插入顺序
是cache,要有大小限定,过期淘汰最后元素,就需要list的顺序性
get, 要刷新状态,把对应的元素提到链表头,也就是用到splice的地方
存两份不合理,保证查找,hash存key 指针,指针指向链表,淘汰的时候移除指针的同时,把hashmap的元素删掉, 这样就维护起来了
代码接口
template<typename K, typename V, size_t Capacity>
class LRUCache {
public:
//Assert that Max size is > 0
static_assert(Capacity > 0);
/*Adds a key=>value item
Returns false if key already exists*/
bool put(const K& k, const V& v);
/*Gets the value for a key.
Returns empty std::optional if not found.
The returned item becomes most-recently-used*/
std::optional<V> get(const K& k);
//Erases an item
void erase(const K& k);
//Utility function.
//Calls callback for each {key,value}
template<typename C>
void forEach(const C& callback) const {
for(auto& [k,v] : items) {
callback(k, v);
}
}
private:
/*std::list stores items (pair<K,V>) in
most-recently-used to least-recently-used order.*/
std::list<std::pair<K,V>> items;
//unordered_map acts as an index to the items store above.
std::unordered_map<K, typename std::list<std::pair<K,V>>::iterator> index;
};
put简单,两个表加一下就行了,如果慢了,拿到表尾,删两个表中的元素
template<typename K, typename V, size_t Capacity>
bool
LRUCache<K,V,Capacity>::put(const K& k, const V& v) {
//Return false if the key already exists
if(index.count(k)) {
return false;
}
//Check if cache is full
if(items.size() == Capacity) {
//Delete the LRU item
index.erase(items.back().first); //Erase the last item key from the map
items.pop_back(); //Evict last item from the list
}
//Insert the new item at front of the list
items.emplace_front(k, v);
//Insert {key->item_iterator} in the map
index.emplace(k, items.begin());
return true;
}
get要做的,拼链表,因为访问到了,要刷新一下
template<typename K, typename V, size_t Capacity>
std::optional<V>
LRUCache<K,V,Capacity>::get(const K& k) {
auto itr = index.find(k);
if(itr == index.end()) {
return {}; //empty std::optional
}
/*Use list splice to transfer this item to
the first position, which makes the item
most-recently-used. Iterators still stay valid.*/
items.splice(items.begin(), items, itr->second);
//从items.begin()这里开始拼接,拼接 items的 itr->second节点 就相当于抽出来拼上
//Return the value in a std::optional
return itr->second->second;
}
erase非常简单,和put差不多,逆向的
template<typename K, typename V, size_t Capacity>
void
LRUCache<K,V,Capacity>::erase(const K& k) {
auto itr = index.find(k);
if(itr == index.end()) {
return;
}
//Erase from the list
items.erase(itr->second);
//Erase from the map
index.erase(itr);
}
这种splice的用法,就是从xx上把iter指向的node偷出来拼到参数指定的位置上,说是拼接,不如说是偷
c++17中,map引入来新方法,extract,也是偷节点
用法
//Ascending order
std::map<int, std::string> m1 = {
{1, "One"}, {2, "Two"}, {3, "Three"} \
};
//Descending order
std::map<int, std::string, std::greater<>> m2 = {
{4, "Four"}, {5, "Five"} \
};
//Print both maps
for(auto [k, v] : m1)
std::cout << v << " "; //One Two Three
for(auto [k, v] : m2)
std::cout << v << " "; //Five Four
//extract from m1 and insert to m2
m2.insert(m1.extract(3));
//get another node from the above node factory
m2.insert(generateNode(6, "Six"));
//Now print m2
for(auto [k, v] : m2)
std::cout << v << " "; //Six Five Four Three
看上去和splice非常像。splice说实话这个参数设计比较复杂,应该设计成extract这样的组合小函数,更清晰一些
参考资料/链接
- https://zh.cppreference.com/w/cpp/container/list/splice
- splice和list::size 有一段历史
- 可以看这篇吐槽 https://blog.csdn.net/russell_tao/article/details/8572000
- 作者实现上的取舍 https://howardhinnant.github.io/On_list_size.html
- 介绍extract https://www.nextptr.com/question/qa1532449120/update-keys-of-map-or-set-with-node-extract
