c++中文件操作的坑
30 Nov 2018
|
|
- 使用ofstream读写文件,记得一定要关闭,否则同进程看不到这个文件的修改内容
std::ofstream f(config_file);
f.write(content.data(), content.size());
// f.close(); // missing!
SomeConfig.Load(config_file); // error, it's empty!
当然,更推荐scope_guard 或者gsl::finally来管理
- stream的继承关系
void foo(const std::istream&) {
puts("istream");
}
void foo(const std::ifstream&) {
puts("ifstream");
}
int main() {
std::fstream t;
foo(t);
}
猜猜调用那个?第一个
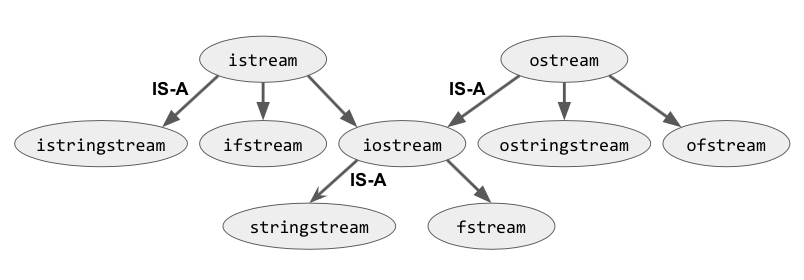
继承关系,深坑
-
stream是有状态的
-
占用很大
using namespace std;
cout<<"std::fstream = "<<sizeof(fstream)<<endl
<<"std::ifstream = "<<sizeof(ifstream)<<endl
<<"std::ofstream = "<<sizeof(ofstream)<<endl;
// std::fstream = 528
// std::ifstream = 520
// std::ofstream = 512
- 检验文件是否存在 ifstream并不怎么快。不过确实挺好用的
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
inline bool exists_test0 (const std::string& name) {
ifstream f(name.c_str());
return f.good();
}
inline bool exists_test1 (const std::string& name) {
if (FILE *file = fopen(name.c_str(), "r")) {
fclose(file);
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
inline bool exists_test2 (const std::string& name) {
return ( access( name.c_str(), F_OK ) != -1 );
}
inline bool exists_test3 (const std::string& name) {
struct stat buffer;
return (stat (name.c_str(), &buffer) == 0);
}
| ifstream | 0.485s |
|---|---|
| FILE fopen | 0.302s |
| posix access() | 0.202s |
| posix stat() | 0.134s |
ref
- https://quuxplusone.github.io/blog/2018/11/26/remember-the-ifstream/
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/90194868
- 检查文件的benchmark代码在这里https://stackoverflow.com/questions/12774207/fastest-way-to-check-if-a-file-exist-using-standard-c-c11-c
- finally https://www.bfilipek.com/2017/04/finalact-follow-up.html
