blog review 第十五期
看tag知内容
Identity Crisis: Sequence v. UUID as Primary Key
Introducing Husky, Datadog’s Third-Generation Event Store
把compact模块单独抠出来了
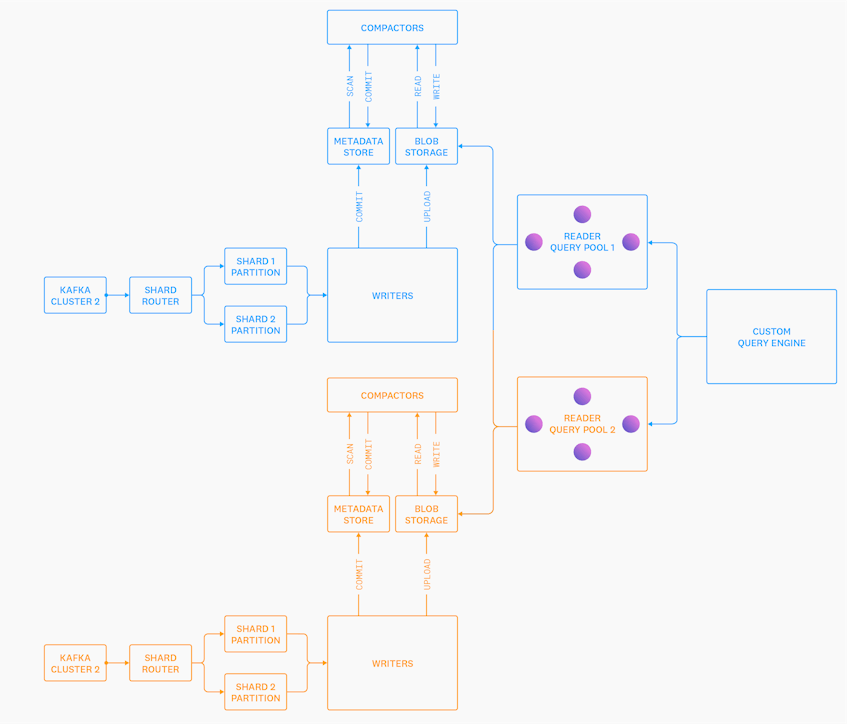
metadata用的FoundationDB
Anna
总结了一下
核心思想是shared nothing + lattice /vector clock解决因果一致性 最终一致性
不是线性的。这种就是欺负人了属于是
lattice
所有的数据都是内存硬抗的,用unordered_map 接口简单,所有的KV编成lattice,这个数据结构也处理冲突问题
- 如何处理冲突?
- actor也就是独立的线程处理具体的key,整体是个hash环,一个线程负责一段CURD信息,各个线程互相通过gossip来沟通信息,收到客户端请求,交流具体的状态信息,判定版本这不是又退化成单线程模式了,为啥比redis快呢?
Vector lock
可以搜SingleKeyCausalLattice和MultiKeyCausalLattice在代码里的用法
LWW更简单,这里直接贴代码
template <typename T>
struct TimestampValuePair {
unsigned long long timestamp{0};
T value;
TimestampValuePair<T>() {
timestamp = 0;
value = T();
}
// need this because of static cast
TimestampValuePair<T>(const unsigned long long& a) {
timestamp = 0;
value = T();
}
TimestampValuePair<T>(const unsigned long long& ts, const T& v) {
timestamp = ts;
value = v;
}
unsigned size() { return value.size() + sizeof(unsigned long long); }
};
template <typename T>
class LWWPairLattice : public Lattice<TimestampValuePair<T>> {
protected:
void do_merge(const TimestampValuePair<T>& p) {
if (p.timestamp >= this->element.timestamp) {
this->element.timestamp = p.timestamp;
this->element.value = p.value;
}
}
public:
LWWPairLattice() : Lattice<TimestampValuePair<T>>(TimestampValuePair<T>()) {}
LWWPairLattice(const TimestampValuePair<T>& p) :
Lattice<TimestampValuePair<T>>(p) {}
MaxLattice<unsigned> size() { return {this->element.size()}; }
};
就是个带时间戳的value
对于这个概念,可以看这个博客https://www.inlighting.org/archives/lamport-timestamp-vector-clock 说的非常好
简单说就是合并对一个key的修改
这里说下bayou和dynamo,都是类似场景,弱一致性,最终一致性,购物车/在线文档修改场景。
bayou https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/401743420
这种同步CRDT数据的代价很大,如果数据规模很大会有通讯风暴,gossip拉胯,dynamo亚马逊只是说一嘴,最终线上用的是paxos改
需要最终一致性的场景也不多
这里能学习的思路也就是各种内存merge动作
序列化反序列化完全依赖RPC框架来做
如何落盘?
本身是分层的,内存层和磁盘层,也有缓存层
if (kSelfTier == Tier::MEMORY) {
MemoryLWWKVS *lww_kvs = new MemoryLWWKVS();
lww_serializer = new MemoryLWWSerializer(lww_kvs);
MemorySetKVS *set_kvs = new MemorySetKVS();
set_serializer = new MemorySetSerializer(set_kvs);
MemoryOrderedSetKVS *ordered_set_kvs = new MemoryOrderedSetKVS();
ordered_set_serializer = new MemoryOrderedSetSerializer(ordered_set_kvs);
MemorySingleKeyCausalKVS *causal_kvs = new MemorySingleKeyCausalKVS();
sk_causal_serializer = new MemorySingleKeyCausalSerializer(causal_kvs);
MemoryMultiKeyCausalKVS *multi_key_causal_kvs =
new MemoryMultiKeyCausalKVS();
mk_causal_serializer =
new MemoryMultiKeyCausalSerializer(multi_key_causal_kvs);
MemoryPriorityKVS *priority_kvs = new MemoryPriorityKVS();
priority_serializer = new MemoryPrioritySerializer(priority_kvs);
} else if (kSelfTier == Tier::DISK) {
lww_serializer = new DiskLWWSerializer(thread_id);
set_serializer = new DiskSetSerializer(thread_id);
ordered_set_serializer = new DiskOrderedSetSerializer(thread_id);
sk_causal_serializer = new DiskSingleKeyCausalSerializer(thread_id);
mk_causal_serializer = new DiskMultiKeyCausalSerializer(thread_id);
priority_serializer = new DiskPrioritySerializer(thread_id);
} else {
内存层就是用unordered map硬抗,disk层如何实现?基于EBS
大开眼界一下
string get(const Key &key, AnnaError &error) {
string res;
LWWValue value;
// open a new filestream for reading in a binary
string fname = ebs_root_ + "ebs_" + std::to_string(tid_) + "/" + key;
std::fstream input(fname, std::ios::in | std::ios::binary);
if (!input) {
error = AnnaError::KEY_DNE;
} else if (!value.ParseFromIstream(&input)) {
std::cerr << "Failed to parse payload." << std::endl;
error = AnnaError::KEY_DNE;
} else {
if (value.value() == "") {
error = AnnaError::KEY_DNE;
} else {
value.SerializeToString(&res);
}
}
return res;
}
unsigned put(const Key &key, const string &serialized) {
LWWValue input_value;
input_value.ParseFromString(serialized);
LWWValue original_value;
string fname = ebs_root_ + "ebs_" + std::to_string(tid_) + "/" + key;
std::fstream input(fname, std::ios::in | std::ios::binary);
if (!input) { // in this case, this key has never been seen before, so we
// attempt to create a new file for it
// ios::trunc means that we overwrite the existing file
std::fstream output(fname,
std::ios::out | std::ios::trunc | std::ios::binary);
if (!input_value.SerializeToOstream(&output)) {
std::cerr << "Failed to write payload." << std::endl;
}
return output.tellp();
} else if (!original_value.ParseFromIstream(
&input)) { // if we have seen the key before, attempt to
// parse what was there before
std::cerr << "Failed to parse payload." << std::endl;
return 0;
} else {
if (input_value.timestamp() >= original_value.timestamp()) {
std::fstream output(fname,
std::ios::out | std::ios::trunc | std::ios::binary);
if (!input_value.SerializeToOstream(&output)) {
std::cerr << "Failed to write payload" << std::endl;
}
return output.tellp();
} else {
return input.tellp();
}
}
}
没错,一个key是一个文件。天才。什么文件整理什么有序无序,我就一个文件爱咋咋地
看数据库代码,我首先会搜fsync和write。这个代码没搜到我还纳闷难道不支持落盘,原来是这么落盘的,佩服
SplinterDB
有点点意思
b tree实际上还是很有搞头的。毕竟已经技术积累了这么多年。局部性好
Many B-trees 这篇文章不错,介绍了b tree的发展,比如betrfs用到的Bε-tree
splinterdb设计了一种数据结构,结合了lsm tree和Bε-tree的优点,叫 STBε-tree
降低写放大
代码在这里 https://github.com/vmware/splinterdb可以研究下
ppt在这里 https://www.usenix.org/system/files/atc20-paper885-slides-conway.pdf,ppt做的非常不错
论文在这里 https://www.usenix.org/system/files/atc20-conway.pdf
本期是AIO专题。我把AIO的资料收集整理了一下
Linux Asynchronous I/O
接口简单
#include <linux/aio_abi.h>
int io_setup(unsigned nr_events, aio_context_t *ctxp);
int io_destroy(aio_context_t ctx);
int io_submit(aio_context_t ctx, long nr, struct iocb **iocbpp);
int io_cancel(aio_context_t ctx, struct iocb *, struct io_event *result);
int io_getevents(aio_context_t ctx, long min_nr, long nr,
struct io_event *events, struct timespec *timeout);
io_setup ctx要初始化,不然会报错(ctx就是个id)
io_submit提交任务 返回值定义
- 返回值等于iocbpp数组个数 理想情况
- 返回值大于0小于iocbpp数组个数,说明失败了
- 返回值小于0
- iocbpp数组有问题
- 第一个iocbpp就直接失败了
io_getevents获取任务 返回值定义
- 返回值等于nr 可能还有任务
- 返回值大于min_nr小于nr,正常返回,无阻塞
- 返回值小于min_nr,阻塞拿到数据
- 返回值小于0 遇到错误
io_event含义
/* read() from /dev/aio returns these structures. */
struct io_event {
__u64 data; /* the data field from the iocb */
__u64 obj; /* what iocb this event came from */
__s64 res; /* result code for this event */
__s64 res2; /* secondary result */
};
iocb
/*
* we always use a 64bit off_t when communicating
* with userland. its up to libraries to do the
* proper padding and aio_error abstraction
*/
struct iocb {
/* these are internal to the kernel/libc. */
__u64 aio_data; /* data to be returned in event's data */
__u32 PADDED(aio_key, aio_reserved1);
/* the kernel sets aio_key to the req # */
/* common fields */
__u16 aio_lio_opcode; /* see IOCB_CMD_ above */
__s16 aio_reqprio;
__u32 aio_fildes;
__u64 aio_buf;
__u64 aio_nbytes;
__s64 aio_offset;
/* extra parameters */
__u64 aio_reserved2; /* TODO: use this for a (struct sigevent *) */
/* flags for the "struct iocb" */
__u32 aio_flags;
/*
* if the IOCB_FLAG_RESFD flag of "aio_flags" is set, this is an
* eventfd to signal AIO readiness to
*/
__u32 aio_resfd;
}; /* 64 bytes */
enum {
IOCB_CMD_PREAD = 0, //pread
IOCB_CMD_PWRITE = 1, //pwrite
IOCB_CMD_FSYNC = 2, // fsync
IOCB_CMD_FDSYNC = 3, //fdatasync 不同步meta,fsync同步所有
/* These two are experimental.
* IOCB_CMD_PREADX = 4,
* IOCB_CMD_POLL = 5,
*/
IOCB_CMD_NOOP = 6,
IOCB_CMD_PREADV = 7,//preadv
IOCB_CMD_PWRITEV = 8,//pwritev
};
/etc/sysctl.conf
fs.aio-max-nr = 1048576
sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.conf
/proc/sys/fs/aio-max-nr
/proc/sys/fs/aio-nr
Linux不同的IO访问方式中,Scylla的选择和依据
| Characteristic | R/W | mmap | DIO | AIO/DIO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cache control | kernel | kernel | user | user |
| Copying | yes | no | no | no |
| MMU activity | low | high | none | none |
| I/O scheduling | kernel | kernel | mixed | user |
| Thread scheduling | kernel | kernel | kernel | user |
| I/O alignment | automatic | automatic | manual | manual |
| Application complexity | low | low | moderate | high |
io_submit,io_getevents被阻塞原因分析
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/100026388 问题相同,都是队列小了
fio测试命令: ./fio -ioengine=libaio -bs=8k -direct=1 -numjobs 16 -rw=read -size=10G -filename=/dev/sda2 -name=”Max throughput” -iodepth=128 -runtime=60
查看系统调用耗时(如果被阻塞,libaio系统调用耗时会比较大,’–duration 1’表示如果系统调用耗时大于1ms则输出):
perf trace -p pidof -s fio –duration 1
查看fio线程被调度出去的原因(即因libaio系统调用被阻塞而被调度出去,该命令打印出调度出去的调用栈):
offcputime -K -p pgrep -nx fio
使用ebpf的bcc工具biolatency来查看后端设备在不同的nr_requests下的压力(即IO在D2C阶段的耗时,其反映了后端设备的性能,本测试中D2C反应的’raid卡+hdd’的性能): biolatency -D
sda请求队列长度128(默认):
cat /sys/block/sda/queue/nr_requests
在fio多任务测试下,由于request资源不够用,导致io_submit系统调用被阻塞在request资源上。
在nr_requests调整为256后,系统调用io_submit几乎不阻塞,在修改为512后,完全不阻塞; 但随着nr_requests加大,io_getevents会越来越阻塞,与io_submit的阻塞情况完全相反
当nr_requests加大,io_getevents会变得阻塞,是因为IO提交流程中request资源充足,io_submit的IO提交流程没有阻塞,造成提交给后端设备的io会很多(通过上述iostat可知sda的请求队列长度随着nr_requests的加大而增大),后端设备处理IO的压力变大(通过上述biolatency -D命令可知D2C耗时随着nr_requests加大而增大),IO完成速率变慢,所以io_getevents需要更多的时间睡眠等待aio完成event。
但总的来说随着nr_requests增大,带宽、iops都变大,性能更好, 但随着nr_requests增大,iops也会线性增长吗,当然不会。设置nr_requests的值时也要考虑到存储设备本身支持的qeueudepth,否则iops反而会下降,
块存储:AIO的直接写流程注释
块存储:AIO的直接读流程注释
块设备异步读page流程
图不错
BLOCK_DUMP观察LINUX IO写入的具体文件
这人博客非常不错
service syslog stop #io干扰
echo 1 > /proc/sys/vm/block_dump
数据压缩
- 对于CPU比较空闲的场景,建议采用压缩率高的
zstd算法。 - 对于CPU比较繁忙的场景,建议采用综合性能比较优异的
lz4算法。
另外文档不错。其实实现是一方面,很多运营经验是很重要的。实现往往是最简单不刺激的。运营才是最刺激的
性能调优检查
#vm.swappiness
sudo sysctl vm.swappiness=0
vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-$(Interface)
echo 4194303 > /proc/sys/kernel/pid_max
cat /proc/meminfo | grep MemTotal | awk '{print $2}
echo ${file-max} > /proc/sys/fs/file-max
/sbin/blockdev --setra /dev/sdb #8192 文件预读
echo deadline > /sys/block/sdb/queue/scheduler # deadline hhd noop ssd
echo 512 > /sys/block/sdb/queue/nr_requests
#关掉irqbalance
systemctl stop irqbalance
systemctl disable irqbalance
#MTU **ip addr**
#rx_buff 8
vi /etc/modprobe.d/hinic.conf
options hinic rx_buff=8
rmmod hinic
modprobe hinic
cat /sys/bus/pci/drivers/hinic/module/parameters/rx_buff
#ring_buffer 4096 ethtool
ethtool -G <网卡名称> rx 4096 tx 4096
ethtool -g <网卡名称>
lro 打开
ethtool -K <网卡名称> lro on
ethtool -k <网卡名称> | grep large-receive-offload
TODO
- https://oceanbase-partner.github.io/lectures-on-dbms-implementation/lecture-1 教程不错
- https://github.com/flower-corp/lotusdb 有点意思
-
https://github.com/hse-project/hse 有点意思
- https://github.com/rizkg/BBHash/tree/alltypes 有点意思
- https://medium.com/indeed-engineering/indeed-mph-fast-and-compact-immutable-key-value-stores-302a1cf2eef0
- https://github.com/indeedeng/mph-table/tree/master/src/main/java/com/indeed/mph 考虑写个c++的
- https://github.com/facebookarchive/LogDevice/blob/main/logdevice/server/storage_tasks/ReadStorageTask.h 有点意思
- Let’s build a distributed Postgres proof of concept很有意思 完全可以用c++胡一个 https://github.com/eatonphil/waterbugdb
