blog review 第十三期
看tag知内容
1,000,000,000 纳秒 = 1秒 三个逗号
内存分配器设计的演进
文章不错
- bump allocator 栈上stack,不过有依赖关系,不能释放老的
- 大小固定?接着realloc,不过缺陷依然存在
- free-list链表组织,常数分配,但是释放也要扫
- size-buckets + free-list 内存块,问题,利用率高了起来,但是缓存不友好
- slab allocator,尽可能的连续分配,组装上面的场景
这里补充一下mimalloc和snmalloc的设计
论文https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/uploads/prod/2019/06/mimalloc-tr-v1.pdf
lock free/线程区分,尽可能不跨。glibc的内存分配是有大锁的,这非常坑爹
https://lobste.rs/s/4awecj/mimalloc_free_list_sharding_action
Mimalloc and snmalloc were written at about the same time by different MSR teams, to solve very different problems, but independently came up with quite different solutions. The main use case for mimalloc was Lean, which is a language that creates a very large number of small objects. The main use case for snmalloc was Verona, a language that (once we finally write a working compiler) will do a lot of allocation and deallocation on different cores (any producer-consumer workload where the producer allocates buffers and the consumer deallocates is a pretty pathological case for most thread-caching allocators). Both ended up with a message-passing design.
The main difference is the recipient of messages. In snmalloc, there’s an allocator that owns chunks and is the only thing that is the target for messages. In mimalloc, the messages are sent directly to the chunk. This means that mimalloc can have less contention on its message queues (unless you have two threads freeing to the same chunk or one thread allocating from a chunk while another is freeing, your message sends are uncontended). In contrast, if two threads are freeing memory allocated by the same thread, you will get some contention on the message queues in snmalloc. This is amortised in snmalloc by the fact that we batch things before sending, so you don’t typically see this contention in practice, and by the fact that our message queues don’t provide any kind of causal ordering guarantees and so can be implemented with a single atomic exchange (so have strong forward-progress guarantees).
Daan was incredibly helpful when he learned about snmalloc and walked us through a whole load of interesting microoptimisations that mimalloc was doing. We’ve incorporated some of those ideas. My favourite one was a mechanism to move a conditional branch off the fast path. When you create a new thread, its TLS contains a pointer to an allocator. We can statically initialise that with a pointer to a global allocator. The global allocator doesn’t own any memory and so you can move the ‘is the TLS pointer initialised to a real allocator’ check to the slow path that you fall into when you can’t allocate any memory (which you always hit in the uninitialised case). In snmalloc this is done with a template function that takes the slow path as a lambda, which makes the lazy-init slow paths very clean (and generates very fast code).
Notes on some PostgreSQL implementation details
- 行锁SELECT FOR UPDATE
-
SELECT FOR SHARE, 引入读写锁,如何表达这些共享的锁?MultiXact - 如何存储锁信息,“SLRU” (“Simple LRU”) stores.
- 如何清理锁信息?VACUUM
剩下的就是关于锁引发的性能问题定位了,我不太懂PG,没认真看
一个数据库阅读列表https://pierrezemb.fr/posts/distsys-resources/
他妈的,永远看不完
gettimeofday() should never be used to measure time
If
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, ...)is not available on your system, then try to find a monotonic clock that is. Likegethrtime()orCLOCK_HIGHRESon Solaris. I have created portable library for getting monotonic time.
rdtsc不行么,虽然只能x86
You can list a directory containing 8 million files! But not with ls.
如果文件多了起来,ls /find根本不行,buffer太小
- 使用getdents
- buffer调大
#define BUF_SIZE 1024*1024*5
-
if(d->d_ino) printf("%sn ", (char *) d->d_name);
The Danger of Atomic Operations
原子操作有风险,一不小心就ABA了,考虑引入RCU
以及列举了一些典型bug
Linux kernel lock-free fd lookup
The bug was introduced on Sep 9, 2005 as part of a migration from a spinlock to RCU refcounting. The change introduced a bug in how the code needs to react on a narrow window of semi-inconsistent state exposed by concurrent updates. It was fixed ten years later, on Jul 1, 2015.
Data Plane Development Kit’s RTE Ring
The bug existed in the first public release of DPDK, which was on Mar 11, 2013. There was a bug with issuing a zero objects dequeue with multiple consumers. It was possible to get more than one thread to succeed the compare-and-set operation and observe starvation or even deadlock in the while loop that checks for preceding dequeues. The same was possible on the enqueue path. The bug was fixed on Mar 22, 2016.
sync.WaitGroup
The bug was introduced on Jul 18, 2011 as part of a WaitGroup rewrite that was intended to improve scalability. The change indeed improved performance and scalability, but it also replaced a simple mutex-based algorithm with a trickier one based on atomic operations. The bug occured in very rare circumstances but led to arbitrary memory corruptions. It was discovered and fixed only on Apr 10, 2014. The bug was caused by an unexpected thread interleaving.
Parallel GC
The bug was introduced on Sep 30, 2011 and fixed only on Jan 15, 2014. The bug led to arbitrary memory corruptions on overloaded machines. The bug was due to unexpected thread interleaving.
org.jctools.maps.NonBlockingHashMap
The bug was introduced sometime before Feb 2009. The bug allowed the remove operation to return the same item more than once, ultimately due to a flaw in the Java CAS spec. It was identified on Jan 15, 2018 and fixed on Jan 21, 2018 after much discussion.
深入理解DPDK程序设计|Linux网络2.0
好长
constexpr
https://github.com/AshleyRoll/squeeze/blob/bd0a263f73246ce9fea13435e8211edd7a368ecd/include/squeeze/nilencoder.h
https://github.com/AshleyRoll/crc_cpp
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tBZ0Z9CVHAM&list=PLHTh1InhhwT6vjwMy3RG5Tnahw0G9qIx6&index=28
rocksdb
https://github.com/facebook/rocksdb/issues/9448
auto tune
-
https://github.com/tikv/tikv/issues/4052
-
https://github.com/tikv/tikv/pull/4335/files
-
https://github.com/tikv/rust-rocksdb/pull/257/files
-
https://www-users.cselabs.umn.edu/Spring-2020/csci5980/final/autotikv.pdf
-
https://pingcap.com/zh/blog/autotikv
-
https://github.com/tikv/auto-tikv
-
https://www.cnblogs.com/pdev/p/11318880.html
-
https://ntnuopen.ntnu.no/ntnu-xmlui/bitstream/handle/11250/2506148/19718_FULLTEXT.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
-
https://csyjia.github.io/csyjia/papers/icdcs20-jia.pdf
auto tune compact
- https://blog.csdn.net/Z_Stand/article/details/113006217
- https://github.com/YanRuizly/rocksdb_autotuned/tree/983381a6a63a7a4c85d40dc4056c83bb69e6bc7c
- https://github.com/hanswilw/rocksdb/pull/1
kvdk
- https://vigourtyy-zhg.blog.csdn.net/article/details/121870619?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
- https://github.com/pmem/kvdk
本文在 Hash 索引部分的介绍仅仅介绍了基本的Hash结构,因为 Hash 结构对 scan 性能并不友好,所以kvdk 还提供了 高性能的prefix-scan 的能力,索引部分的bucket 变更成为了跳表,并且会持久化最后一层跳表结构,高层指针仍然保存在DRAM 中。
有意思
Ribbon filter
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.02515.pdf
https://blog.csdn.net/Z_Stand/article/details/119979663
Ribbon filter的全称是Rapid Incremental Boolean Banding ON the fly ,能够基于真值矩阵 高效得用增量方式构建过滤器。 相比于传统的Bloom Filter 来说,它的核心差异以及 优势主要是如下几点:
- 采用XOR 方式进行按位匹配。而大多数的bloom filter都是ADD 方式进行按位匹配。
- ribbon filter的构成是 在原始key经过多个hash函数之后 由一个二维bit数组组成,并不是像传统的filter 由一个bit数组组成。
- 对CPU cache 更友好,检查一个key 是否在filter内部,ribbon filter 可以直接加载二位数组中的一个bit数组进行顺序匹配,而传统ADD filter则需要一个bit数组上根据hash函数的结果随机匹配。
- 对空间更友好,ribbon filter存储二位数组时可以通过高斯消元法转化成上三角矩阵,更利于压缩;且加载到内存中也更利于计算。
- 消耗更多的CPU,因为ribbon filter 优化的主体是节约内存 以及 磁盘存储,而因为需要针对二维矩阵的后台计算(高斯消元),相比于传统一维数组来说会消耗更多的CPU。
论文以及代码
Ribbon filter: practically smaller than Bloom and Xor https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.02515 Xor filter: Faster and Smaller Than Bloom and Cuckoo Filters https://www.researchgate.net/publication/339921464_Xor_Filters_Faster_and_Smaller_Than_Bloom_and_Cuckoo_Filters xor-filter implemetation http://web.stanford.edu/class/archive/cs/cs166/cs166.1216/lectures/13/Slides13.pdf#page=49 All filter code https://github.com/FastFilter/fastfilter_cpp
Trie
-
Adaptive Radix Tree
另外 radix_tree就是PATRICIA trie
一个基本实现https://github.com/ytakano/radix_tree
也可以看redis的实现
论文https://db.in.tum.de/~leis/papers/ART.pdf
一个实现 https://github.com/laurynas-biveinis/unodb/
优化epoch https://github.com/laurynas-biveinis/unodb/pull/286/files
优化细节 https://of-code.blogspot.com/2021/12/lock-free-quiescent-state-based.html
背后的原理https://preshing.com/20160726/using-quiescent-states-to-reclaim-memory/
SURF
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/38385054
代码https://github.com/efficient/SuRF
论文 https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~huanche1/publications/surf_paper.pdf
fiber
- https://github.com/romange/gaia
- http://www.romange.com/2018/12/15/introduction-to-fibers-in-c-/
NuRaft
https://github.com/eBay/NuRaft/pull/36/files
https://github.com/eBay/NuRaft/commit/1b08f254fb646eeb7f21175ff866661d986d593c
https://tech.ebayinc.com/engineering/nuraft-a-lightweight-c-raft-core/
https://github.com/greensky00/latency-collector/tree/master/src
https://github.com/datatechnology/cornerstone
RBB以及背后的HAMT
Improving RRB-Tree Performance through Transience https://hypirion.com/thesis.pdf
Persistence for the Masses: RRB-Vectors in a Systems Language https://public.sinusoid.es/misc/immer/immer-icfp17.pdf
https://michael.steindorfer.name/publications/oopsla15.pdf
原理https://lrita.github.io/2018/07/15/hash-tree-hamp/
c++代码https://github.com/chaelim/HAMT/blob/master/include/HashTrie.h
RAMP-TAO: Layering Atomic Transactions on Facebook’s Online TAO Data Store
直接在TAO的基础上把RAMP协议实现了
主要动机
一半写成功一半写失败的问题以及读到了前面更新失败的写,归根结底是事务匮乏
引入原子性失败和原子性可见,说白了就是事务
几个解决方案,单点写+广播,不太行,2PC,不能保证原子可见,后台数据校正修复(根据已有的数据做checker),不通用
- 选择隔离级别
满足原子可见的最低标准,Read Atomic isolation即可,不需要SI这么复杂,但RC是解决不了原子可见问题的
自然就用到RAMP这个协议Read Atomic Multiple Partition
In the first round, RAMP sends out read requests for all data items and detects nonatomic readsWhich could happen if only part of another transaction’s writes were visible. . In the second round, the algorithm explicitly repairs these reads by fetching any missing versions. RAMP writers use a modified two-phase commit protocol that requires metadata to be attached to each update, similar to the mechanism used by cross-shard write transactions on TAO.
怎么说呢,读,加check,查所有的读,判断是否满足原子读,写,走2pc
但是在TAO上实践还是很有难度的
- 所有的动作都用上这个RAMP协议,不一定啊,客户端不更新不就用不上了。这就要求不能让客户端强依赖
- RAMP的metadata,需要考虑分布式系统的复制问题,这无异降低了可用性
- RAMP假定数据多版本,且可用 ,TAO一条数据就一个版本(就没版本这个概念不就得了)
如何解决?
- 内部库RefillLibrary,解决RAMP 的metadata复制分布/可用性问题,感觉就是另一种etcd/zookeeper管理
TAO: Facebook’s Distributed Data Store for the Social Graph
“The Associations and Objects”.
对象和关系。感觉用kv就能描述,比如用户是对象,用户和用户的关注是关系
读优化的一个图数据库,重点 1处理大量读请求,以及如何扩展(scale)
如何表达图,TAO用的edge list而不是邻接矩阵邻接表
[ [0,1], [0,6], [0,8], [1,4], [1,6], [1,9], [2,4], [2,6], [3,4], [3,5],
[3,8], [4,5], [4,9], [7,8], [7,9] ]
整体架构两层
一层cache一层 数据库,数据库用的mysql
mysql要分片,对象和关系用不同的表。感觉有点拿mysql当kv用的感觉了,如果是基于myrocks的话实际上也可以,性能不差,感觉更可以直接用KV table存储来做
cache层重点设计,因为要满足强可读
设计了三点, cache servers, cache tiers, and leader/follower tiers.
cache tiers就是cache servers组成的组,且支持组间主从,从只读
cache避免空key的缓存击穿,可以抽象成promise,Thundering Herds & Promises 用folly::promise 这个点子挺奇妙
之所以有这个东西,是facebook业务场景主要是查,空查,比如用户喜好
如何扩展?主要思路就是不同区域有多个组,然后把写入转发到主区域的leader,然后从无限扩,知道主节点转发给主
raft的复制,一个leader N个learner是不是就是类似的东西
Difference between Apache parquet and arrow
高赞写的不错,arrow是内存,落地可以转成Parquet
How to efficiently load data to memory
切分CPU和IO任务。我看folly就不错
Postgres Indexes for Newbies
Five Tips For a Healthier Postgres Database in the New Year
不提内容哈,像crunchydata这种公司怎么挣钱的,这个面相的工作面也太小了点
utf8mb4, because utf8 was taken
Mysql 别用utf8 3byte
TCP吞吐性能缺陷的根源
quic基于udp,没有滑动窗口
glibc内存管理ptmalloc源代码分析
https://paper.seebug.org/papers/Archive/refs/heap/glibc%E5%86%85%E5%AD%98%E7%AE%A1%E7%90%86ptmalloc%E6%BA%90%E4%BB%A3%E7%A0%81%E5%88%86%E6%9E%90.pdf

这个文档旧了,最新的设计引入了tcache 具体可以看这个英文文档https://sourceware.org/glibc/wiki/MallocInternals
这里也提了一嘴https://zhenghaodong.github.io/2018/01/19/2019-02-07-Glibc-ptmalloc/
tlsf
https://github.com/mattconte/tlsf/blob/master/tlsf.c
http://www.gii.upv.es/tlsf/main/docs
http://www.gii.upv.es/tlsf/files/papers/tlsf_slides.pdf 一个分配器,针对实时系统的,代码不长
这个ppt有点意思
Peeking under the hood of GCC’s __builtin_expect
#define unlikely(expr) __builtin_expect(!!(expr), 0)
#define likely(expr) __builtin_expect(!!(expr), 1)
这个大家都知道,但原理是什么呢?
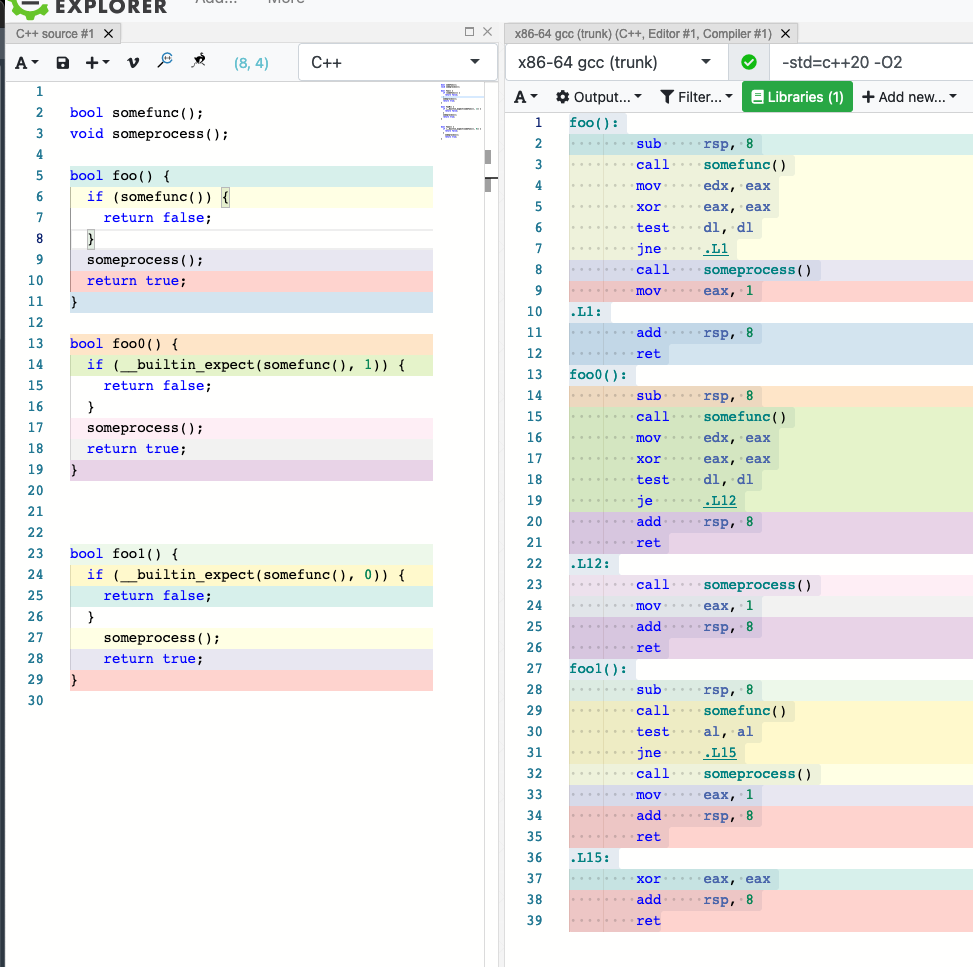
看这个图就明白了,如果简单的条件,三个函数都会优化成一样的,但是这种有函数调用,无法优化的,likely会优化成je,unlikely会优化成jne
CPU的分支预测很影响性能,(可以看这个了解影响https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/22469702)
If one digs deep enough in the Intel 64 and IA-32 Architectures Optimization Reference Manual, one can find a reference for this behaviour on page 105 (emphasis mine):
3.4.1.6 Branch Type Selection
The default predicted target for indirect branches and calls is the fall-through path. Fall-through prediction is overridden if and when a hardware prediction is available for that branch. The predicted branch target from branch prediction hardware for an indirect branch is the previously executed branch target.
The more you know.
简单说就是流水线的分支预测默认走fall-through,也就是不判定直接执行,然后检查确定条件,如果条件不满足就等于重来,branch-miss,这里的je/jne就相当于给一个流水走的默认分支,有不同权重的路径
使用 shared_ptr 线程间共享配置
省掉一个锁
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <chrono>
#include <thread>
#include <memory>
#include <atomic>
#include <random>
using namespace std::chrono_literals;
class Config {
public:
int id;
Config(int id) {
this->id = id;
std::cout << "[" << std::this_thread::get_id() << "] " << id << " created" << std::endl;
std::cout.flush();
}
~Config() {
std::cout << "[" << std::this_thread::get_id() << "] " << id << " deleted" << std::endl;
std::cout.flush();
}
};
std::shared_ptr<Config> globalCfg;
std::shared_ptr<Config> readCurrentCfg() {
return std::atomic_load(&globalCfg);
}
void reader() {
std::mt19937 rng;
rng.seed(std::random_device()());
std::uniform_int_distribution<std::mt19937::result_type> dist(100, 20 * 100);
auto cfg = readCurrentCfg();
std::cout << "[" << std::this_thread::get_id() << "] " << cfg->id << " accessed" << std::endl;
std::cout.flush();
std::this_thread::sleep_for(1ms * dist(rng));
std::cout << "[" << std::this_thread::get_id() << "] " << cfg->id << " accessed again" << std::endl;
std::cout.flush();
}
void updateConfig(int id) {
auto cfg = std::make_shared<Config>(id);
std::atomic_store(&globalCfg, cfg);
}
void writer() {
std::mt19937 rng;
rng.seed(std::random_device()());
std::uniform_int_distribution<std::mt19937::result_type> dist(100, 5 * 100);
for (int i = 1; i <= 15; i++) {
std::this_thread::sleep_for(1ms * dist(rng));
updateConfig(i);
}
}
int main() {
globalCfg = std::make_shared<Config>(0);
std::mt19937 rng;
rng.seed(std::random_device()());
std::uniform_int_distribution<std::mt19937::result_type> dist(20, 100);
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<std::thread>> threads;
threads.push_back(std::make_unique<std::thread>(writer));
for (int i = 1; i <= 30; i++) {
threads.push_back(std::make_unique<std::thread>(reader));
std::this_thread::sleep_for(1ms * dist(rng));
}
for (auto& thread : threads) {
thread->join();
}
return 0;
}
Throw away the keys: Easy, Minimal Perfect Hashing
之前搜gperf-tools tcmalloc无意间搜到gpref GNU perfect hash function generator
没想过啥场景能用上这玩意,后来在facebook的库proxygen里遇到了。一个完美hash生成器的场景,就是映射表,映射表本身只读,不会发生更改,这样的映射函数不发生冲突,这样最终效果就像数组一样,性能O1
c++也有一个库,实现了类似 的逻辑,https://github.com/serge-sans-paille/frozen/blob/master/include/frozen/unordered_map.h
引用的文章就是这篇文章
一种通用的C++无侵入单元测试方法
公司内网帖子,挺有意思
就是说,mock,被mock的接口不是虚函数,没法继承mock,要是引入一个公共基类,又有点过度设计(for tests only)
直接宏替换!
比如
class Foo {
public:
Foo() {
proxy_ = client.GetProxy<BarProxy>("service_name");
}
~Foo();
void DoSomethingWithProxy();
private:
std::shared_ptr<BarProxy> proxy_;
};
BarProxy长这样bar_proxy.h
class BarProxy : public ServiceProxy final {
public:
BarProxy() {}
~BarProxy() override = default;
Status Command(const ContextPtr& context, Reply* reply, const std::string& cmd);
};
这里的BarProxy的Command没法直接mock,继承也比较恶心,直接宏替换!
mock的代码 bar_proxy_mock.h
#pragma once
#include "gmock/gmock.h"
// 必须include再定义宏,否则这个头文件的名字就被替换了
#include "bar_proxy.h"
#define BarProxy BarProxyMock
class BarProxyMock : public ServiceProxy {
public:
BarProxyMock() {
codec_.reset(new trpc::RedisClientCodec());
option_.reset(new trpc::ServiceProxyOption());
}
~RedisServiceProxyMock() = default;
MOCK_METHOD(Status, Command,
(const ContextPtr& context, Reply* reply, const std::string& cmd));
};
单测代码
#include "bar_proxy_mock.h"
#include "foo.cc"
#include "gtest/gtest.h"
TEST(Foo, DoSomethingWithProxy) {
Foo foo
foo.DoSomethingWithProxy();
}
todo
公司网打不开
https://minimalmodeling.substack.com/p/migrations-migrating-attributes-pt-ade
https://minimalmodeling.substack.com/p/migrations-migrating-attributes-pt
整理的不错 https://github.com/jackwaudby/dbordb
wiretigerhttps://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzU4MTA2NTM0Ng==&mid=2247486965&idx=2&sn=3158498b756daea079c80ec2f39be2c8&chksm=fd4c0218ca3b8b0e13c417dfd9e67b458e48d007be0d692c32bc7cda4fbf66a4befaab7b6102&scene=21#wechat_redirect
博客不错
https://nbjl.nankai.edu.cn/12124/list.htm
