a little order delving into the stl sorting algorithms
演讲主题是对比std::sort std::partial_sort std::nth_elemet的速度
直接说结论吧。ppt很长,90页,介绍了一些benchmark工具和网站
std::sort O(N*log(N))
std::partial_sort O(N*log(K)) 可能退化成O(N) 最差持平std::sort
std::nth_element +sort O(N+k*log(k)) 可能退化成O(N) 最差持平std::sort
排序一部分
条件,100万元素,按照排序子集个数作图
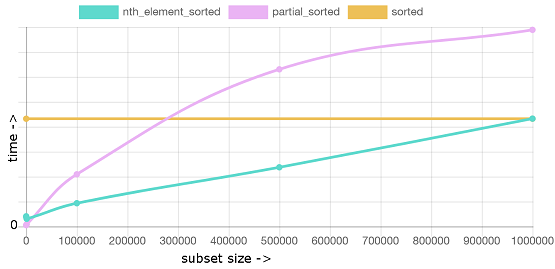
在小的数据级下std::partial_sort非常可观
容器
条件,排100元素,使用容量不同的容器
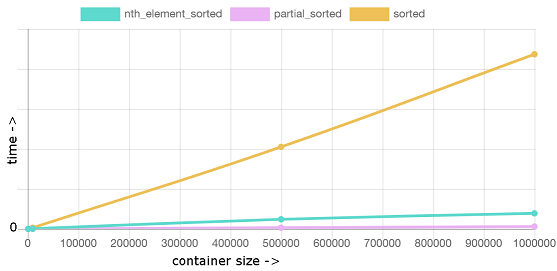
同上,std::partial_sort 非常可观
两种场景结合
条件,容器容量变化,排N/5个元素
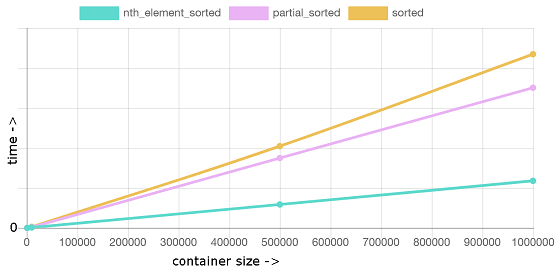
同样,std::partial_sort吊打 要明白场景
结论: 搜子集优先用std::parital_sort,其次用std::nth_element + std::sort
背后的原因
std::sort实现原理 源码见参考链接2
template<typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Compare>
inline void
__sort(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last,
_Compare __comp)
{
if (__first != __last)
{
std::__introsort_loop(__first, __last,
std::__lg(__last - __first) * 2,
__comp);
std::__final_insertion_sort(__first, __last, __comp);
}
}
主要是introsort和insert sort
introsort是quicksort和heapsort的结合体,quicksort在较差的场景下退化为O(N2)heapsort排序稳定但是能优化的场景下有多余动作,所以introsort结合两者,先递归2*log(N)层,如果没排序成功在调用heapsort,整体O(N*log(N))
参考下面的分析,总结下(这是个paper实现)
- 在数据量很大时采用正常的快速排序,此时效率为O(logN)。
- 一旦分段后的数据量小于某个阈值,就改用插入排序,因为此时这个分段是基本有序的,这时效率可达O(N)。
- 在递归过程中,如果递归层次过深,分割行为有恶化倾向时,它能够自动侦测出来,使用堆排序来处理,在此情况下,使其效率维持在堆排序的O(N logN),但这又比一开始使用堆排序好
std::nth_element 见参考链接3
template<typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Compare>
inline void
nth_element(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __nth,
_RandomAccessIterator __last, _Compare __comp)
{
// concept requirements...
if (__first == __last || __nth == __last) return;
std::__introselect(__first, __nth, __last,
std::__lg(__last - __first) * 2,
__gnu_cxx::__ops::__iter_comp_iter(__comp));
}
类似sort introselect实现是 quickselect+heapselect
quickselect需要选pivot,然后其他类似quicksort,到nth结束。收敛的快一些
heapselect就是个建堆选择的过程 复杂度 O(N*log(k))
std::partial_sort heap_select+heap sort
template<typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Compare>
inline void
__partial_sort(_RandomAccessIterator __first,
_RandomAccessIterator __middle,
_RandomAccessIterator __last,
_Compare __comp)
{
std::__heap_select(__first, __middle, __last, __comp);
std::__sort_heap(__first, __middle, __comp);
}
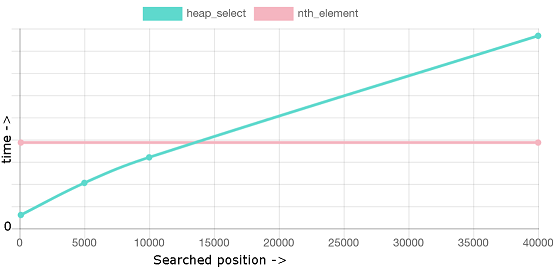
为什么heapsort反而比introsort快?主要在于heap_select
reference
- https://github.com/CppCon/CppCon2018/tree/master/Presentations/a_little_order_delving_into_the_stl_sorting_algorithms
- std::sort https://github.com/gcc-mirror/gcc/blob/3f7d0abcd22f9a797ea496688cbda746466f0f54/libstdc%2B%2B-v3/include/bits/stl_algo.h#L1952
- std::nth_element https://github.com/gcc-mirror/gcc/blob/3f7d0abcd22f9a797ea496688cbda746466f0f54/libstdc%2B%2B-v3/include/bits/stl_algo.h#L4772
- std::partial_sort https://github.com/gcc-mirror/gcc/blob/e352c93463fe598ace13d8a017c7c86e535f1065/libstdc%2B%2B-v3/include/bits/stl_algo.h#L1917
- 这个std::sort分析写的不错<
- https://liam.page/2018/09/18/std-sort-in-STL/>
- http://feihu.me/blog/2014/sgi-std-sort/
- llvm的实现以及优化好像又不大一样 https://blog.0xbbc.com/2017/01/analysis-of-std-sort-function/
或者到博客上提issue 我能收到邮件提醒。
