googletest使用记录/checklist/以及遇到的一个奇怪的问题
14 Sep 2017
|
|
[toc]
有一个玩转GoogleTest的文章讲的不错,值得花点时间看下
指定测试捕获catch
gdb /path/to/test
catch throw
r --gtest_filter='Test.Testcase' --gmock_verbose=info
bt
一些使用方法
最近使用googletest,新加了单元测试,就需要判定开关单元测试对原来测试的影响,做个记录
./db_iterator_test --gtest_filter=-DBIteratorTestInstance/DBIteratorTest.IterSeekBeforePrevWithTimestamp/*
过滤用例,也可以代码中加DISABLED_
TEST(FooTest, DISABLED_DoesAbc) { ... }
过滤多个用例,匹配模式之间用分好隔开
./table_test --gtest_filter=*FilterBlockInBlockCache:*BasicBlockBasedTableProperties
测试的准备工作 针对testsuits
全局预设定, 实现下面的接口,一个testsuit执行一次,可以实现
static void SetUpTestSuite() {}
static void TearDownTestSuite() {}
注意是static
针对每一个小测试,实现下面的接口,每个test_f都会执行一次
virtual void SetUp() {}
virtual void TearDown() {}
gmock
常用
using ::testing::Return;
using ::testing::_;
InSequence实现DAG菱形结构,拆分成一条一条的拼起来就行
InSequence s1, s2;
EXPECT_CALL(_, A()).InSequence(s1, s2);
EXPECT_CALL(_, B1()).InSequence(s1 );
EXPECT_CALL(_, B2()).InSequence( s2);
EXPECT_CALL(_, C()).InSequence(s1, s2);
gdb调试googletest
gdb --args db_iterator_test --gtest_filter=-DBIteratorTestInstance/DBIteratorTest.IterSeekBeforePrevWithTimestamp/1
打断点有点麻烦,得nm抓符号名,一般都是类名/单元测试类名字_TestBody
gtest命令行
测试案例输出
| 命令行参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| –gtest_color=(yes|no|auto) | 输出命令行时是否使用一些五颜六色的颜色。默认是auto。 |
| –gtest_print_time | 输出命令行时是否打印每个测试案例的执行时间。默认是不打印的。 |
| –gtest_output=xml[:DIRECTORY_PATH|:FILE_PATH] | 将测试结果输出到一个xml中。1.–gtest_output=xml: 不指定输出路径时,默认为案例当前路径。 2.–gtest_output=xml:d:\ 指定输出到某个目录 3.–gtest_output=xml:d:\foo.xml 指定输出到d:\foo.xml 如果不是指定了特定的文件路径,gtest每次输出的报告不会覆盖,而会以数字后缀的方式创建。xml的输出内容后面介绍吧。 |
对案例的异常处理
| 命令行参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| –gtest_break_on_failure | 调试模式下,当案例失败时停止,方便调试 |
| –gtest_throw_on_failure | 当案例失败时以C++异常的方式抛出 |
| –gtest_catch_exceptions | 是否捕捉异常。gtest默认是不捕捉异常的,因此假如你的测试案例抛了一个异常,很可能会弹出一个对话框,这非常的不友好,同时也阻碍了测试案例的运行。如果想不弹这个框,可以通过设置这个参数来实现。如将–gtest_catch_exceptions设置为一个非零的数。注意:这个参数只在Windows下有效。 |
说到问题,有这么个测试错误,应该是key1后面多了一串0
db/db_log_iter_test.cc:280: Failure
Value of: handler.seen
Actual: "Put(1, key1\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0, 1024)Put(0, key2\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0, 1024)LogData(blob1\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0)Put(1, key3\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0, 1024)LogData(blob2\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0)Delete(0, key2\0\0\0\0\0\0\0\0)"
Expected: "Put(1, key1, 1024)" "Put(0, key2, 1024)" "LogData(blob1)" "Put(1, key3, 1024)" "LogData(blob2)" "Delete(0, key2)"
Which is: "Put(1, key1, 1024)Put(0, key2, 1024)LogData(blob1)Put(1, key3, 1024)LogData(blob2)Delete(0, key2)"
[ FAILED ] DBTestXactLogIterator.TransactionLogIteratorBlobs (102 ms)
这两个是同一个字符串
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <iomanip>
std::string s1="Put(1, key1, 1024)" "Put(0, key2, 1024)" "LogData(blob1)" "Put(1, key3, 1024)" "LogData(blob2)" "Delete(0, key2)";
std::string s2="Put(1, key1, 1024)Put(0, key2, 1024)LogData(blob1)Put(1, key3, 1024)LogData(blob2)Delete(0, key2)";
int main()
{
bool b = s1==s2;
std::cout<<std::boolalpha << b << std::endl;// true
}
EXCEPT_EQ
#define GTEST_ASSERT_EQ(expected, actual) \
ASSERT_PRED_FORMAT2(::testing::internal:: \
EqHelper<GTEST_IS_NULL_LITERAL_(expected)>::Compare, \
expected, actual)
//这个宏展开就是f(#a,#b,a,b)
//EqHelper 偏特化 如果是null就是eqhelper<true>
template <bool lhs_is_null_literal>
class EqHelper {
public:
// This templatized version is for the general case.
template <typename T1, typename T2>
static AssertionResult Compare(const char* expected_expression,
const char* actual_expression,
const T1& expected,
const T2& actual) {
return CmpHelperEQ(expected_expression, actual_expression, expected,
actual);
}
// With this overloaded version, we allow anonymous enums to be used
// in {ASSERT|EXPECT}_EQ when compiled with gcc 4, as anonymous
// enums can be implicitly cast to BiggestInt.
//
// Even though its body looks the same as the above version, we
// cannot merge the two, as it will make anonymous enums unhappy.
static AssertionResult Compare(const char* expected_expression,
const char* actual_expression,
BiggestInt expected,
BiggestInt actual) {
return CmpHelperEQ(expected_expression, actual_expression, expected,
actual);
}
};
// This specialization is used when the first argument to ASSERT_EQ()
// is a null pointer literal, like NULL, false, or 0.
template <>
class EqHelper<true> {
public:
// We define two overloaded versions of Compare(). The first
// version will be picked when the second argument to ASSERT_EQ() is
// NOT a pointer, e.g. ASSERT_EQ(0, AnIntFunction()) or
// EXPECT_EQ(false, a_bool).
template <typename T1, typename T2>
static AssertionResult Compare(
const char* expected_expression,
const char* actual_expression,
const T1& expected,
const T2& actual,
// The following line prevents this overload from being considered if T2
// is not a pointer type. We need this because ASSERT_EQ(NULL, my_ptr)
// expands to Compare("", "", NULL, my_ptr), which requires a conversion
// to match the Secret* in the other overload, which would otherwise make
// this template match better.
typename EnableIf<!is_pointer<T2>::value>::type* = 0) {
return CmpHelperEQ(expected_expression, actual_expression, expected,
actual);
}
// This version will be picked when the second argument to ASSERT_EQ() is a
// pointer, e.g. ASSERT_EQ(NULL, a_pointer).
template <typename T>
static AssertionResult Compare(
const char* expected_expression,
const char* actual_expression,
// We used to have a second template parameter instead of Secret*. That
// template parameter would deduce to 'long', making this a better match
// than the first overload even without the first overload's EnableIf.
// Unfortunately, gcc with -Wconversion-null warns when "passing NULL to
// non-pointer argument" (even a deduced integral argument), so the old
// implementation caused warnings in user code.
Secret* /* expected (NULL) */,
T* actual) {
// We already know that 'expected' is a null pointer.
return CmpHelperEQ(expected_expression, actual_expression,
static_cast<T*>(NULL), actual);
}
};
//核心就是这个了
// The helper function for {ASSERT|EXPECT}_EQ.
template <typename T1, typename T2>
AssertionResult CmpHelperEQ(const char* expected_expression,
const char* actual_expression,
const T1& expected,
const T2& actual) {
GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_PUSH_(4389 /* signed/unsigned mismatch */)
if (expected == actual) {
return AssertionSuccess();
}
GTEST_DISABLE_MSC_WARNINGS_POP_()
return CmpHelperEQFailure(expected_expression, actual_expression, expected,
actual);
}
const std::string& 在gtest使用中出现的一个奇怪的堆栈
#0 0x00000000004f6e33 in __gnu_cxx::__atomic_add (
__mem=0x7fffbf8c46ac <testing::internal::HandleSehExceptionsInMethodIfSupported<testing::Test, void>(testing::Test*, void (testing::Test::*)(), char const*)+93>, __val=1) at /usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/7/../../../../include/c++/7/ext/atomicity.h:53
#1 0x00000000004f6ef3 in __gnu_cxx::__atomic_add_dispatch (
__mem=0x7fffbf8c46ac <testing::internal::HandleSehExceptionsInMethodIfSupported<testing::Test, void>(testing::Test*, void (testing::Test::*)(), char const*)+93>, __val=1) at /usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/7/../../../../include/c++/7/ext/atomicity.h:96
#2 0x00000000005034fa in std::string::_Rep::_M_refcopy (
this=0x7fffbf8c469c <testing::internal::HandleSehExceptionsInMethodIfSupported<testing::Test, void>(testing::Test*, void (testing::Test::*)(), char const*)+77>) at /usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/7/../../../../include/c++/7/bits/basic_string.h:3265
#3 0x0000000000500802 in std::string::_Rep::_M_grab (
this=0x7fffbf8c469c <testing::internal::HandleSehExceptionsInMethodIfSupported<testing::Test, void>(testing::Test*, void (testing::Test::*)(), char const*)+77>, __alloc1=..., __alloc2=...) at /usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/7/../../../../include/c++/7/bits/basic_string.h:3223
#4 0x00000000004fe2b8 in std::string::assign (this=0x7fffffffdd98, __str=...)
at /usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/7/../../../../include/c++/7/bits/basic_string.tcc:699
#5 0x00000000004fdddf in std::string::operator= (this=0x7fffffffdd98, __str=...)
at /usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/7/../../../../include/c++/7/bits/basic_string.h:3629
测试常用小代码段
- 随机生成字符串
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
std::string random_string(size_t length = 10) {
auto randchar = []() -> char
{
const char charset[] =
"0123456789"
"ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"
"abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz";
const size_t max_index = (sizeof(charset) - 1);
return charset[ rand() % max_index ];
};
std::string str(length,0);
std::generate_n( str.begin(), length, randchar );
return str;
}
INSTANTIATE_TEST_CASE_P 生成参数组合用例
另外,单元测试太多,写了个小脚本,抓出失败的
#!/bin/bash
for file in *test
do
./$file > /dev/null 2>&1
if [[ $? != 0 ]]
then
echo $file
fi
done
事件监听器?testing::TestEventListener 没用过
执行原理,一图流
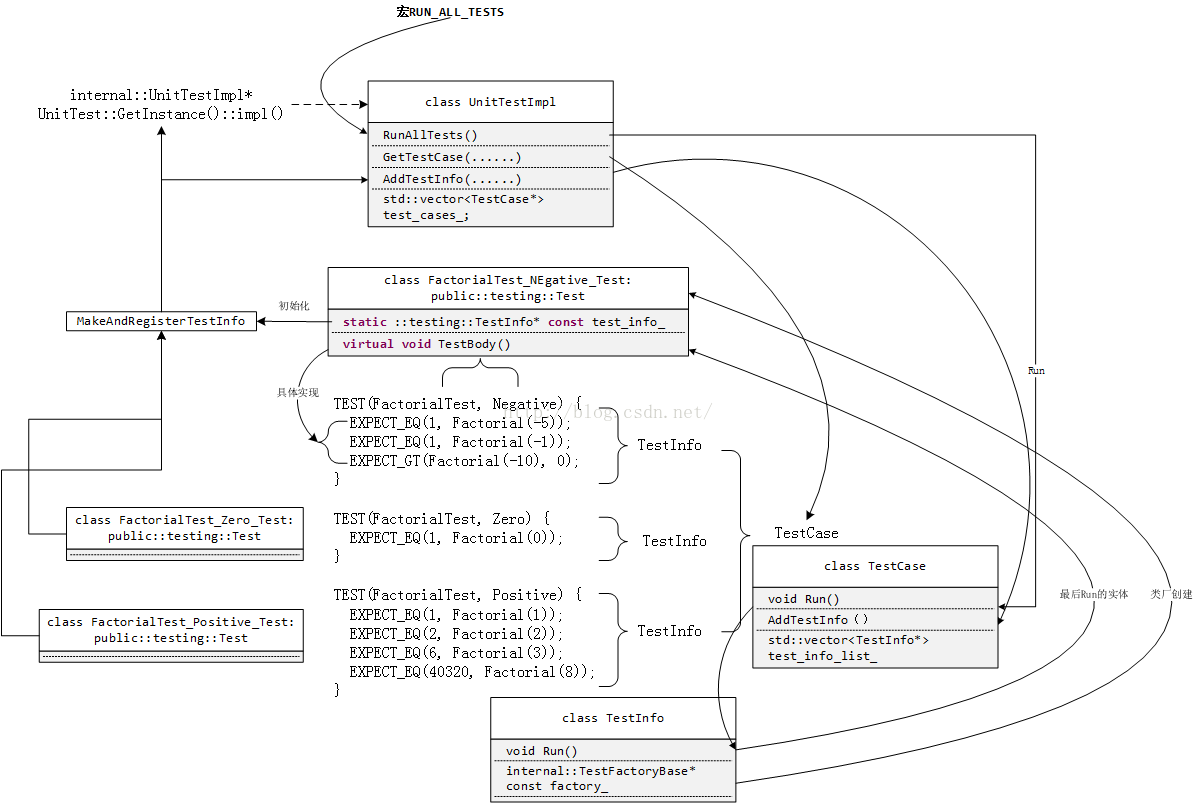
参考
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/14018434/how-to-specify-multiple-exclusion-filters-in-gtest-filter/14619685
- http://www.cnblogs.com/coderzh/archive/2009/04/10/1432789.html
- 跳过用例 https://stackoverflow.com/questions/7208070/googletest-how-to-skip-a-test
- setup执行一次 就是setupsuites https://stackoverflow.com/questions/29968219/call-code-only-once-in-gtest-per-class
- https://github.com/seznam/httpmockserver 这有个httpserver mock 有点意思

 } class DISABLED_BarTest : public testing::Test {
} class DISABLED_BarTest : public testing::Test { 